- java.lang.Object
-
- picocli.CommandLine
-
public class CommandLine extends Object
CommandLine interpreter that uses reflection to initialize an annotated user object with values obtained from the command line arguments.
The full user manual is hosted at https://picocli.info.
Example
An example that implements
Callableand uses theCommandLine.executeconvenience API to run in a single line of code:@Command(name = "checksum", mixinStandardHelpOptions = true, version = "checksum 4.0", description = "Prints the checksum (SHA-1 by default) of a file to STDOUT.") class CheckSum implements Callable<Integer> { @Parameters(index = "0", description = "The file whose checksum to calculate.") private File file; @Option(names = {"-a", "--algorithm"}, description = "MD5, SHA-1, SHA-256, ...") private String algorithm = "SHA-1"; @Override public Integer call() throws Exception { // your business logic goes here... byte[] fileContents = Files.readAllBytes(file.toPath()); byte[] digest = MessageDigest.getInstance(algorithm).digest(fileContents); System.out.printf("%0" + (digest.length*2) + "x%n", new BigInteger(1,digest)); return 0; } // CheckSum implements Callable, so parsing, error handling and handling user // requests for usage help or version help can be done with one line of code. public static void main(String[] args) { int exitCode = new CommandLine(new CheckSum()).execute(args); System.exit(exitCode); } }Another example where the application calls
parseArgsand takes responsibility for error handling and checking whether the user requested help:import static picocli.CommandLine.*; @Command(mixinStandardHelpOptions = true, version = "v3.0.0", header = "Encrypt FILE(s), or standard input, to standard output or to the output file.") public class Encrypt { @Parameters(description = "Any number of input files") private List<File> files = new ArrayList<File>(); @Option(names = { "-o", "--out" }, description = "Output file (default: print to console)") private File outputFile; @Option(names = { "-v", "--verbose"}, description = "Verbose mode. Helpful for troubleshooting. Multiple -v options increase the verbosity.") private boolean[] verbose; }Use
CommandLineto initialize a user object as follows:public static void main(String... args) { Encrypt encrypt = new Encrypt(); try { ParseResult parseResult = new CommandLine(encrypt).parseArgs(args); if (!CommandLine.printHelpIfRequested(parseResult)) { runProgram(encrypt); } } catch (ParameterException ex) { // command line arguments could not be parsed System.err.println(ex.getMessage()); ex.getCommandLine().usage(System.err); } }Invoke the above program with some command line arguments. The below are all equivalent:
--verbose --out=outfile in1 in2 --verbose --out outfile in1 in2 -v --out=outfile in1 in2 -v -o outfile in1 in2 -v -o=outfile in1 in2 -vo outfile in1 in2 -vo=outfile in1 in2 -v -ooutfile in1 in2 -vooutfile in1 in2
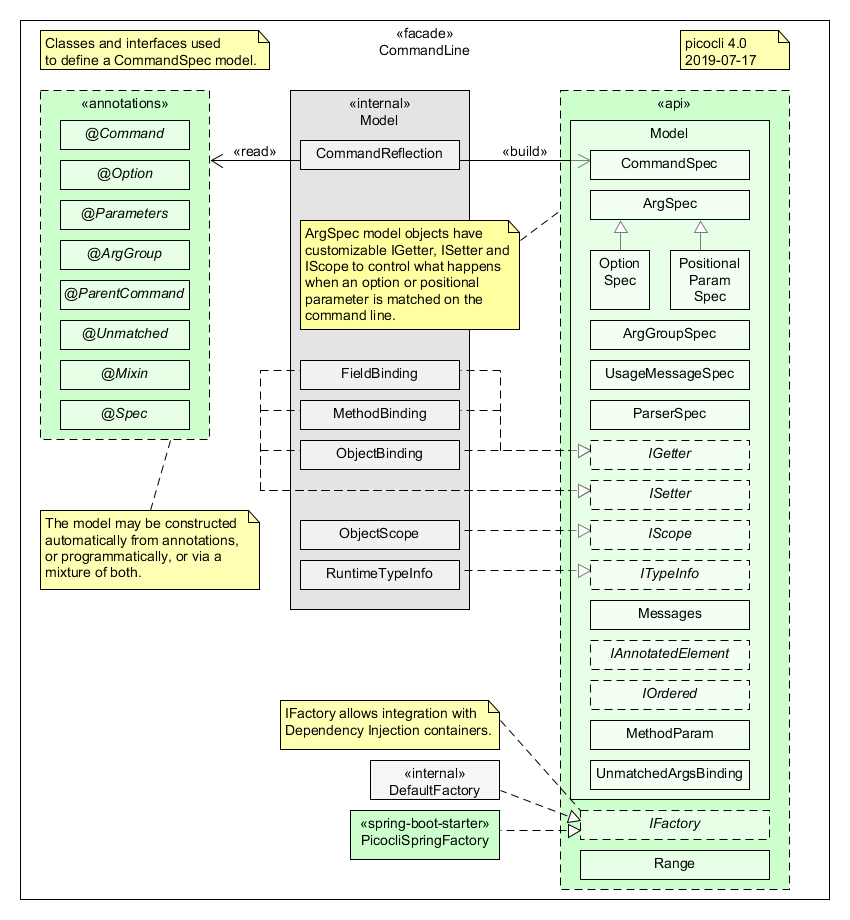
Classes and Interfaces for Defining a CommandSpec Model
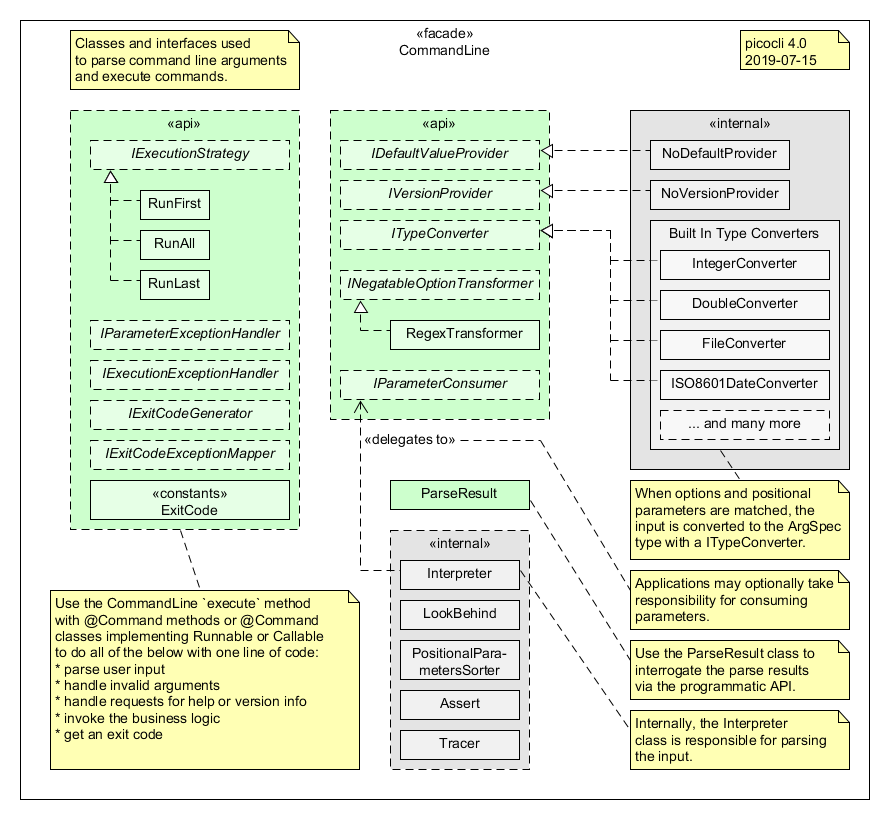
Classes Related to Parsing Command Line Arguments
-
-
Nested Class Summary
Nested Classes Modifier and Type Class and Description static classCommandLine.AbstractHandler<R,T extends CommandLine.AbstractHandler<R,T>>Deprecated.static classCommandLine.AbstractParseResultHandler<R>static interfaceCommandLine.ArgGroupACommandmay define one or moreArgGroups: a group of options, positional parameters or a mixture of the two.static interfaceCommandLine.CommandAnnotate your class with@Commandwhen you want more control over the format of the generated help message.static classCommandLine.DefaultExceptionHandler<R>Deprecated.static classCommandLine.DuplicateNameExceptionException indicating that multiple named elements have incorrectly used the same name.static classCommandLine.DuplicateOptionAnnotationsExceptionException indicating that multiple fields have been annotated with the same Option name.static classCommandLine.ExecutionExceptionException indicating a problem while invoking a command or subcommand.static classCommandLine.ExitCodeDefines some exit codes used by picocli as default return values from theexecuteandexecuteHelpRequestmethods.static classCommandLine.HelpA collection of methods and inner classes that provide fine-grained control over the contents and layout of the usage help message to display to end users when help is requested or invalid input values were specified.static classCommandLine.HelpCommandHelp command that can be installed as a subcommand on all application commands.static interfaceCommandLine.IDefaultValueProviderProvides default value for a command.static interfaceCommandLine.IExceptionHandlerstatic interfaceCommandLine.IExceptionHandler2<R>static interfaceCommandLine.IExecutionExceptionHandlerClasses implementing this interface know how to handle Exceptions that occurred while executing theRunnable,CallableorMethoduser object of the command.static interfaceCommandLine.IExecutionStrategyImplementations are responsible for "executing" the user input and returning an exit code.static interfaceCommandLine.IExitCodeExceptionMapperInterface that provides the appropriate exit code that will be returned from theexecutemethod for an exception that occurred during parsing or while invoking the command's Runnable, Callable, or Method.static interfaceCommandLine.IExitCodeGenerator@Command-annotated classes can implement this interface to specify an exit code that will be returned from theexecutemethod when the command is successfully invoked.static interfaceCommandLine.IFactoryFactory for instantiating classes that are registered declaratively with annotation attributes, likeCommandLine.Command.subcommands(),CommandLine.Option.converter(),CommandLine.Parameters.converter()andCommandLine.Command.versionProvider().static interfaceCommandLine.IHelpCommandInitializableDeprecated.useCommandLine.IHelpCommandInitializable2insteadstatic interfaceCommandLine.IHelpCommandInitializable2Help commands that provide usage help for other commands can implement this interface to be initialized with the information they need.static interfaceCommandLine.IHelpFactoryCreates theCommandLine.Helpinstance used to render the usage help message.static interfaceCommandLine.IHelpSectionRendererRenders a section of the usage help message.static interfaceCommandLine.IModelTransformerProvides a way to modify how the command model is built.static interfaceCommandLine.INegatableOptionTransformerDetermines the option name transformation of negatable boolean options.static classCommandLine.InitializationExceptionException indicating a problem duringCommandLineinitialization.static interfaceCommandLine.IParameterConsumerOptions or positional parameters can be assigned aIParameterConsumerthat implements custom logic to process the parameters for this option or this position.static interfaceCommandLine.IParameterExceptionHandlerClasses implementing this interface know how to handleParameterExceptions(usually from invalid user input).static interfaceCommandLine.IParameterPreprocessorOptions, positional parameters and commands can be assigned aIParameterPreprocessorthat implements custom logic to preprocess the parameters for this option, position or command.static interfaceCommandLine.IParseResultHandlerDeprecated.UseCommandLine.IExecutionStrategyinstead.static interfaceCommandLine.IParseResultHandler2<R>Deprecated.useCommandLine.IExecutionStrategyinstead, seeexecute(String...)static interfaceCommandLine.ITypeConverter<K>When parsing command line arguments and initializing fields annotated with@Optionor@Parameters, String values can be converted to any type for which aITypeConverteris registered.static interfaceCommandLine.IVersionProviderProvides version information for a command.static classCommandLine.MaxValuesExceededExceptionException indicating that more values were specified for an option or parameter than itsarityallows.static classCommandLine.MissingParameterExceptionException indicating that a required parameter was not specified.static classCommandLine.MissingTypeConverterExceptionException indicating that an annotated field had a type for which noCommandLine.ITypeConverterwas registered.static interfaceCommandLine.MixinFields annotated with@Mixinare "expanded" into the current command:@Optionand@Parametersin the mixin class are added to the options and positional parameters of this command.static classCommandLine.ModelThis class provides a namespace for classes and interfaces that model concepts and attributes of command line interfaces in picocli.static classCommandLine.MutuallyExclusiveArgsExceptionException indicating that the user input included multiple arguments from a mutually exclusive group.static interfaceCommandLine.OptionAnnotate fields in your class with@Optionand picocli will initialize these fields when matching arguments are specified on the command line.static classCommandLine.OverwrittenOptionExceptionException indicating that an option for a single-value option field has been specified multiple times on the command line.static classCommandLine.ParameterExceptionException indicating something went wrong while parsing command line options.static classCommandLine.ParameterIndexGapExceptionException indicating that there was a gap in the indices of the fields annotated withCommandLine.Parameters.static interfaceCommandLine.ParametersFields annotated with@Parameterswill be initialized with positional parameters.static interfaceCommandLine.ParentCommandFields annotated with@ParentCommandwill be initialized with the parent command of the current subcommand.static classCommandLine.ParseResultEncapsulates the result of parsing an array of command line arguments.static classCommandLine.PicocliExceptionBase class of all exceptions thrown bypicocli.CommandLine.static classCommandLine.PropertiesDefaultProviderIDefaultValueProviderimplementation that loads default values for command line options and positional parameters from a properties file orPropertiesobject.static classCommandLine.RangeDescribes the number of parameters required and accepted by an option or a positional parameter.static classCommandLine.RegexTransformerA regular expression-based option name transformation for negatable options.static classCommandLine.RunAllCommand line execution strategy that prints help if requested, and otherwise executes the top-level command and all subcommands asRunnable,CallableorMethod.static classCommandLine.RunFirstCommand line execution strategy that prints help if requested, and otherwise executes the top-levelRunnableorCallablecommand.static classCommandLine.RunLastCommand line execution strategy that prints help if requested, and otherwise executes the most specificRunnableorCallablesubcommand.static classCommandLine.ScopeTypeSpecifies the scope of the element.static interfaceCommandLine.SpecFields annotated with@Specwill be initialized with theCommandSpecfor the command the field is part of.static classCommandLine.TraceLevelEnumerates over the trace level values for filtering which internal debug statements should be printed.static classCommandLine.TracerUtility class for printing internal debug statements.static classCommandLine.TypeConversionExceptionException thrown byCommandLine.ITypeConverterimplementations to indicate a String could not be converted.static interfaceCommandLine.UnmatchedFields annotated with@Unmatchedwill be initialized with the list of unmatched command line arguments, if any.static classCommandLine.UnmatchedArgumentExceptionException indicating that a command line argument could not be mapped to any of the fields annotated withCommandLine.OptionorCommandLine.Parameters.static classCommandLine.UseDefaultConverterConverter that can be used to signal to picocli that it should use the default converter.
-
Field Summary
Fields Modifier and Type Field and Description static StringVERSIONThis is picocli version "4.7.7".
-
Constructor Summary
Constructors Constructor and Description CommandLine(Object command)Constructs a newCommandLineinterpreter with the specified object (which may be an annotated user object or aCommandSpec) and a default factory.CommandLine(Object command, CommandLine.IFactory factory)Constructs a newCommandLineinterpreter with the specified object (which may be an annotated user object or aCommandSpec) and object factory.
-
Method Summary
All Methods Static Methods Instance Methods Concrete Methods Deprecated Methods Modifier and Type Method and Description CommandLineaddMixin(String name, Object mixin)Adds the options and positional parameters in the specified mixin to this command.CommandLineaddSubcommand(Object command)Registers a subcommand with the name obtained from the@Command(name = "...")annotation attribute of the specified command.CommandLineaddSubcommand(String name, Object command)Registers a subcommand with the specified name.CommandLineaddSubcommand(String name, Object command, String... aliases)Registers a subcommand with the specified name and all specified aliases.static <C extends Callable<T>,T>
Tcall(Class<C> callableClass, CommandLine.IFactory factory, PrintStream out, CommandLine.Help.Ansi ansi, String... args)Deprecated.useexecute(String...)andgetExecutionResult()insteadstatic <C extends Callable<T>,T>
Tcall(Class<C> callableClass, CommandLine.IFactory factory, PrintStream out, PrintStream err, CommandLine.Help.Ansi ansi, String... args)Deprecated.useexecute(String...)andgetExecutionResult()insteadstatic <C extends Callable<T>,T>
Tcall(Class<C> callableClass, CommandLine.IFactory factory, PrintStream out, String... args)Deprecated.useexecute(String...)andgetExecutionResult()insteadstatic <C extends Callable<T>,T>
Tcall(Class<C> callableClass, CommandLine.IFactory factory, String... args)Deprecated.useexecute(String...)andgetExecutionResult()insteadstatic <C extends Callable<T>,T>
Tcall(C callable, PrintStream out, CommandLine.Help.Ansi ansi, String... args)Deprecated.useexecute(String...)andgetExecutionResult()insteadstatic <C extends Callable<T>,T>
Tcall(C callable, PrintStream out, PrintStream err, CommandLine.Help.Ansi ansi, String... args)Deprecated.useexecute(String...)andgetExecutionResult()insteadstatic <C extends Callable<T>,T>
Tcall(C callable, PrintStream out, String... args)Deprecated.useexecute(String...)andgetExecutionResult()insteadstatic <C extends Callable<T>,T>
Tcall(C callable, String... args)Deprecated.useexecute(String...)andgetExecutionResult()insteadvoidclearExecutionResults()Clears the execution result of a previous invocation from thisCommandLineand all subcommands.static CommandLine.DefaultExceptionHandler<List<Object>>defaultExceptionHandler()Convenience method that returnsnew DefaultExceptionHandler<List<Object>>().static CommandLine.IFactorydefaultFactory()Returns the defaultCommandLine.IFactoryimplementation used if no factory was specified in theCommandLine constructor.intexecute(String... args)Convenience method to allow command line application authors to avoid some boilerplate code in their application.static IntegerexecuteHelpRequest(CommandLine.ParseResult parseResult)Helper method that may be useful when processing theParseResultthat results from successfully parsing command line arguments.CharactergetAtFileCommentChar()Returns the character that starts a single-line comment ornullif all content of argument files should be interpreted as arguments (without comments).CommandLine.Help.ColorSchemegetColorScheme()Returns the color scheme to use when printing help.<T> TgetCommand()Returns the annotated user object that thisCommandLineinstance was constructed with.static List<Method>getCommandMethods(Class<?> cls, String methodName)Helper to get methods of a class annotated with@Commandvia reflection, optionally filtered by method name (not@Command.name).StringgetCommandName()Returns the command name (also called program name) displayed in the usage help synopsis.CommandLine.Model.CommandSpecgetCommandSpec()Returns theCommandSpecmodel that thisCommandLinewas constructed with.CommandLine.IDefaultValueProvidergetDefaultValueProvider()Returns the default value provider for the command, ornullif none has been set.StringgetEndOfOptionsDelimiter()Returns the end-of-options delimiter that signals that the remaining command line arguments should be treated as positional parameters.PrintWritergetErr()Returns the writer to use when printing diagnostic (error) messages during command execution.CommandLine.IExecutionExceptionHandlergetExecutionExceptionHandler()Returns the handler for dealing with exceptions that occurred in theCallable,RunnableorMethoduser object of a command when the command was executed.<T> TgetExecutionResult()Returns the result of calling the user objectCallableor invoking the user objectMethodafter parsing the user input, ornullif this command has not been executed or if thisCommandLineis for a subcommand that was not specified by the end user on the command line.CommandLine.IExecutionStrategygetExecutionStrategy()Returns the execution strategy used by theexecutemethod to invoke the business logic on the user objects of this command and/or the user-specified subcommand(s).CommandLine.IExitCodeExceptionMappergetExitCodeExceptionMapper()Returns the mapper that was set by the application to map from exceptions to exit codes, for use by theexecutemethod.CommandLine.IFactorygetFactory()Returns the factory that thisCommandLinewas constructed with.CommandLine.HelpgetHelp()Returns a newHelpobject created by theIHelpFactorywith theCommandSpecandColorSchemeof this command.CommandLine.IHelpFactorygetHelpFactory()Returns theIHelpFactorythat is used to construct the usage help message.List<String>getHelpSectionKeys()Returns the section keys in the order that the usage help message should render the sections.Map<String,CommandLine.IHelpSectionRenderer>getHelpSectionMap()Returns the map of section keys and renderers used to construct the usage help message.Map<String,Object>getMixins()Returns a map of user objects whose options and positional parameters were added to ("mixed in" with) this command.CommandLine.INegatableOptionTransformergetNegatableOptionTransformer()Returns theINegatableOptionTransformerused to create the negative form of negatable options.PrintWritergetOut()Returns the writer used when printing user-requested usage help or version help during command execution.CommandLine.IParameterExceptionHandlergetParameterExceptionHandler()Returns the handler for dealing with invalid user input when the command is executed.CommandLinegetParent()Returns the command that this is a subcommand of, ornullif this is a top-level command.CommandLine.ParseResultgetParseResult()ResourceBundlegetResourceBundle()Returns the ResourceBundle of this command ornullif no resource bundle is set.StringgetSeparator()Returns the String that separates option names from option values when parsing command line options.Map<String,CommandLine>getSubcommands()Returns a map with the subcommands registered on this instance.List<String>getUnmatchedArguments()Returns the list of unmatched command line arguments, if any.intgetUsageHelpLongOptionsMaxWidth()Returns the maximum usage help long options column max width to the specified value.intgetUsageHelpWidth()Returns the maximum width of the usage help message.StringgetUsageMessage()Similar tousage(PrintStream), but returns the usage help message as a String instead of printing it to thePrintStream.StringgetUsageMessage(CommandLine.Help.Ansi ansi)Similar tousage(PrintStream, Help.Ansi), but returns the usage help message as a String instead of printing it to thePrintStream.StringgetUsageMessage(CommandLine.Help.ColorScheme colorScheme)Similar tousage(PrintStream, Help.ColorScheme), but returns the usage help message as a String instead of printing it to thePrintStream.static Objectinvoke(String methodName, Class<?> cls, PrintStream out, CommandLine.Help.Ansi ansi, String... args)Deprecated.useexecute(String...)andgetExecutionResult()insteadstatic Objectinvoke(String methodName, Class<?> cls, PrintStream out, PrintStream err, CommandLine.Help.Ansi ansi, String... args)Deprecated.useexecute(String...)andgetExecutionResult()insteadstatic Objectinvoke(String methodName, Class<?> cls, PrintStream out, String... args)Deprecated.useexecute(String...)andgetExecutionResult()insteadstatic Objectinvoke(String methodName, Class<?> cls, String... args)Deprecated.useexecute(String...)andgetExecutionResult()insteadbooleanisAbbreviatedOptionsAllowed()Returns whether abbreviation of option names should be allowed when matching options.booleanisAbbreviatedSubcommandsAllowed()Returns whether abbreviation of subcommands should be allowed when matching subcommands.booleanisAdjustLineBreaksForWideCJKCharacters()Returns whether line breaks should take wide Chinese, Japanese and Korean characters into account for line-breaking purposes.booleanisAllowOptionsAsOptionParameters()Returns whether options can have parameter values that match the name of an option in this command, or whether such values should be rejected with a missing parameter exception.booleanisAllowSubcommandsAsOptionParameters()Returns whether options can have parameter values that match subcommand names or aliases, or whether such values should be rejected with a missing parameter exception.booleanisCaseInsensitiveEnumValuesAllowed()Returns whether the parser should ignore case when converting arguments toenumvalues.booleanisExpandAtFiles()Returns whether arguments starting with'@'should be treated as the path to an argument file and its contents should be expanded into separate arguments for each line in the specified file.booleanisInterpolateVariables()Returns whether variables should be interpolated in String values.booleanisOptionsCaseInsensitive()Returns whether upper case and lower case should be ignored when matching option names.booleanisOverwrittenOptionsAllowed()Returns whether options for single-value fields can be specified multiple times on the command line.booleanisPosixClusteredShortOptionsAllowed()Returns whether the parser accepts clustered short options.booleanisSplitQuotedStrings()Deprecated.Most applications should not change the default. The rare application that does need to split parameter values without respecting quotes should useCommandLine.Model.ParserSpec.splitQuotedStrings(boolean).booleanisStopAtPositional()Returns whether the parser interprets the first positional parameter as "end of options" so the remaining arguments are all treated as positional parameters.booleanisStopAtUnmatched()Returns whether the parser should stop interpreting options and positional parameters as soon as it encounters an unmatched option.booleanisSubcommandsCaseInsensitive()Returns whether upper case and lower case should be ignored when matching subcommands.booleanisToggleBooleanFlags()Returns whether the value of boolean flag options should be "toggled" when the option is matched.booleanisTrimQuotes()Returns whether the parser should trim quotes from command line arguments.booleanisUnmatchedArgumentsAllowed()Returns whether the end user may specify arguments on the command line that are not matched to any option or parameter fields.booleanisUnmatchedOptionsAllowedAsOptionParameters()Returns whether options can have parameter values that resemble an option, or whether such values should be rejected as unknown options.booleanisUnmatchedOptionsArePositionalParams()Returns whether arguments on the command line that resemble an option should be treated as positional parameters.booleanisUsageHelpAutoWidth()Returns whether picocli should attempt to detect the terminal size and adjust the usage help message width to take the full terminal width.booleanisUsageHelpRequested()Returnstrueif an option annotated withCommandLine.Option.usageHelp()was specified on the command line.booleanisUseSimplifiedAtFiles()Returns whether to use a simplified argument file format that is compatible with JCommander.booleanisVersionHelpRequested()Returnstrueif an option annotated withCommandLine.Option.versionHelp()was specified on the command line.List<CommandLine>parse(String... args)Deprecated.useparseArgs(String...)insteadCommandLine.ParseResultparseArgs(String... args)Expands any @-files in the specified command line arguments, then parses the arguments and returns aParseResultwith the options, positional parameters, and subcommands (if any) that were recognized and initialized during the parsing process.<R> RparseWithHandler(CommandLine.IParseResultHandler2<R> handler, String[] args)Deprecated.useexecute(String...)andgetExecutionResult()insteadList<Object>parseWithHandler(CommandLine.IParseResultHandler handler, PrintStream out, String... args)Deprecated.useexecute(String...)andgetExecutionResult()instead<R> RparseWithHandlers(CommandLine.IParseResultHandler2<R> handler, CommandLine.IExceptionHandler2<R> exceptionHandler, String... args)Deprecated.useexecute(String...)andgetExecutionResult()insteadList<Object>parseWithHandlers(CommandLine.IParseResultHandler handler, PrintStream out, CommandLine.Help.Ansi ansi, CommandLine.IExceptionHandler exceptionHandler, String... args)Deprecated.useexecute(String...)andgetExecutionResult()insteadstatic <T> TpopulateCommand(T command, String... args)Convenience method that initializes the specified annotated object from the specified command line arguments.static <T> TpopulateSpec(Class<T> spec, String... args)Convenience method that derives the command specification from the specified interface class, and returns an instance of the specified interface.static booleanprintHelpIfRequested(CommandLine.ParseResult parseResult)Delegates toexecuteHelpRequest(ParseResult).static booleanprintHelpIfRequested(List<CommandLine> parsedCommands, PrintStream out, CommandLine.Help.Ansi ansi)Deprecated.useprintHelpIfRequested(ParseResult)insteadstatic booleanprintHelpIfRequested(List<CommandLine> parsedCommands, PrintStream out, PrintStream err, CommandLine.Help.Ansi ansi)Deprecated.useexecuteHelpRequest(ParseResult)insteadstatic booleanprintHelpIfRequested(List<CommandLine> parsedCommands, PrintStream out, PrintStream err, CommandLine.Help.ColorScheme colorScheme)Deprecated.useexecuteHelpRequest(ParseResult)insteadvoidprintVersionHelp(PrintStream out)Delegates toprintVersionHelp(PrintStream, Help.Ansi)with the ANSI setting of the configured color scheme.voidprintVersionHelp(PrintStream out, CommandLine.Help.Ansi ansi)Prints version information from theCommandLine.Command.version()annotation to the specifiedPrintStream.voidprintVersionHelp(PrintStream out, CommandLine.Help.Ansi ansi, Object... params)Prints version information from theCommandLine.Command.version()annotation to the specifiedPrintStream.voidprintVersionHelp(PrintWriter out)Delegates toprintVersionHelp(PrintWriter, Help.Ansi, Object...)with the ANSI setting of the configured color scheme.voidprintVersionHelp(PrintWriter out, CommandLine.Help.Ansi ansi, Object... params)Prints version information from theCommandLine.Command.version()annotation to the specifiedPrintWriter.<K> CommandLineregisterConverter(Class<K> cls, CommandLine.ITypeConverter<K> converter)Registers the specified type converter for the specified class.static <R extends Runnable>
voidrun(Class<R> runnableClass, CommandLine.IFactory factory, PrintStream out, CommandLine.Help.Ansi ansi, String... args)Deprecated.useexecute(String...)insteadstatic <R extends Runnable>
voidrun(Class<R> runnableClass, CommandLine.IFactory factory, PrintStream out, PrintStream err, CommandLine.Help.Ansi ansi, String... args)Deprecated.useexecute(String...)insteadstatic <R extends Runnable>
voidrun(Class<R> runnableClass, CommandLine.IFactory factory, PrintStream out, String... args)Deprecated.useexecute(String...)insteadstatic <R extends Runnable>
voidrun(Class<R> runnableClass, CommandLine.IFactory factory, String... args)Deprecated.useexecute(String...)insteadstatic <R extends Runnable>
voidrun(R runnable, PrintStream out, CommandLine.Help.Ansi ansi, String... args)Deprecated.useexecute(String...)insteadstatic <R extends Runnable>
voidrun(R runnable, PrintStream out, PrintStream err, CommandLine.Help.Ansi ansi, String... args)Deprecated.useexecute(String...)insteadstatic <R extends Runnable>
voidrun(R runnable, PrintStream out, String... args)Deprecated.useexecute(String...)insteadstatic <R extends Runnable>
voidrun(R runnable, String... args)Deprecated.useexecute(String...)insteadCommandLinesetAbbreviatedOptionsAllowed(boolean newValue)Sets whether abbreviated option names should be matched.CommandLinesetAbbreviatedSubcommandsAllowed(boolean newValue)Sets whether abbreviated subcommands should be matched.CommandLinesetAdjustLineBreaksForWideCJKCharacters(boolean adjustForWideChars)Sets whether line breaks should take wide Chinese, Japanese and Korean characters into account, and returns this UsageMessageSpec.CommandLinesetAllowOptionsAsOptionParameters(boolean newValue)Sets whether options can have parameter values that match the name of an option in this command, or whether such values should be rejected with a missing parameter exception.CommandLinesetAllowSubcommandsAsOptionParameters(boolean newValue)Sets whether options can have parameter values that match subcommand names or aliases, or whether such values should be rejected with a missing parameter exception.CommandLinesetAtFileCommentChar(Character atFileCommentChar)Sets the character that starts a single-line comment ornullif all content of argument files should be interpreted as arguments (without comments).CommandLinesetCaseInsensitiveEnumValuesAllowed(boolean newValue)Sets whether the parser should ignore case when converting arguments toenumvalues.CommandLinesetColorScheme(CommandLine.Help.ColorScheme colorScheme)Sets the color scheme to use when printing help.CommandLinesetCommandName(String commandName)Sets the command name (also called program name) displayed in the usage help synopsis to the specified value.CommandLinesetDefaultValueProvider(CommandLine.IDefaultValueProvider newValue)Sets a default value provider for the command and sub-commandsCommandLinesetEndOfOptionsDelimiter(String delimiter)Sets the end-of-options delimiter that signals that the remaining command line arguments should be treated as positional parameters.CommandLinesetErr(PrintWriter err)Sets the writer to use when printing diagnostic (error) messages during command execution.CommandLinesetExecutionExceptionHandler(CommandLine.IExecutionExceptionHandler executionExceptionHandler)Sets a custom handler for dealing with exceptions that occurred in theCallable,RunnableorMethoduser object of a command when the command was executed via the execute method.voidsetExecutionResult(Object result)Sets the result of calling the business logic on the command's user object.CommandLinesetExecutionStrategy(CommandLine.IExecutionStrategy executionStrategy)Sets the execution strategy that theexecutemethod should use to invoke the business logic on the user objects of this command and/or the user-specified subcommand(s).CommandLinesetExitCodeExceptionMapper(CommandLine.IExitCodeExceptionMapper exitCodeExceptionMapper)Sets the mapper used by theexecutemethod to map exceptions to exit codes.CommandLinesetExpandAtFiles(boolean expandAtFiles)Sets whether arguments starting with'@'should be treated as the path to an argument file and its contents should be expanded into separate arguments for each line in the specified file.CommandLinesetHelpFactory(CommandLine.IHelpFactory helpFactory)Sets a newIHelpFactoryto customize the usage help message.CommandLinesetHelpSectionKeys(List<String> keys)Sets the section keys in the order that the usage help message should render the sections.CommandLinesetHelpSectionMap(Map<String,CommandLine.IHelpSectionRenderer> map)Sets the map of section keys and renderers used to construct the usage help message.CommandLinesetInterpolateVariables(boolean interpolate)Sets whether variables should be interpolated in String values.CommandLinesetNegatableOptionTransformer(CommandLine.INegatableOptionTransformer transformer)Sets theINegatableOptionTransformerused to create the negative form of negatable options.CommandLinesetOptionsCaseInsensitive(boolean newValue)Sets whether upper case and lower case should be ignored when matching option names.CommandLinesetOut(PrintWriter out)Sets the writer to use when printing user-requested usage help or version help during command execution.CommandLinesetOverwrittenOptionsAllowed(boolean newValue)Sets whether options for single-value fields can be specified multiple times on the command line without aCommandLine.OverwrittenOptionExceptionbeing thrown.CommandLinesetParameterExceptionHandler(CommandLine.IParameterExceptionHandler parameterExceptionHandler)Sets the handler for dealing with invalid user input when the command is executed.CommandLinesetPosixClusteredShortOptionsAllowed(boolean newValue)Sets whether short options like-x -v -f SomeFilecan be clustered together like-xvfSomeFile.CommandLinesetResourceBundle(ResourceBundle bundle)Sets the ResourceBundle containing usage help message strings.CommandLinesetSeparator(String separator)Sets the String the parser uses to separate option names from option values to the specified value.CommandLinesetSplitQuotedStrings(boolean newValue)Deprecated.Most applications should not change the default. The rare application that does need to split parameter values without respecting quotes should useCommandLine.Model.ParserSpec.splitQuotedStrings(boolean).CommandLinesetStopAtPositional(boolean newValue)Sets whether the parser interprets the first positional parameter as "end of options" so the remaining arguments are all treated as positional parameters.CommandLinesetStopAtUnmatched(boolean newValue)Sets whether the parser should stop interpreting options and positional parameters as soon as it encounters an unmatched option.CommandLinesetSubcommandsCaseInsensitive(boolean newValue)Sets whether upper case and lower case should be ignored when matching subcommands.CommandLinesetToggleBooleanFlags(boolean newValue)Sets whether the value of boolean flag options should be "toggled" when the option is matched.CommandLinesetTrimQuotes(boolean newValue)Sets whether the parser should trim quotes from command line arguments before processing them.CommandLinesetUnmatchedArgumentsAllowed(boolean newValue)Sets whether the end user may specify unmatched arguments on the command line without aCommandLine.UnmatchedArgumentExceptionbeing thrown.CommandLinesetUnmatchedOptionsAllowedAsOptionParameters(boolean newValue)Sets whether options can have parameter values that resemble an option, or whether such values should be rejected as unknown options.CommandLinesetUnmatchedOptionsArePositionalParams(boolean newValue)Sets whether arguments on the command line that resemble an option should be treated as positional parameters.CommandLinesetUsageHelpAutoWidth(boolean detectTerminalSize)Sets whether picocli should attempt to detect the terminal size and adjust the usage help message width to take the full terminal width.CommandLinesetUsageHelpLongOptionsMaxWidth(int columnWidth)Returns the maximum usage help long options column max width to the specified value.CommandLinesetUsageHelpWidth(int width)Sets the maximum width of the usage help message.CommandLinesetUseSimplifiedAtFiles(boolean simplifiedAtFiles)Sets whether to use a simplified argument file format that is compatible with JCommander.static CommandLine.Tracertracer()Returns theTracerused internally for printing internal debug statements.static voidusage(Object command, PrintStream out)Equivalent tonew CommandLine(command).usage(out).static voidusage(Object command, PrintStream out, CommandLine.Help.Ansi ansi)Equivalent tonew CommandLine(command).usage(out, ansi).static voidusage(Object command, PrintStream out, CommandLine.Help.ColorScheme colorScheme)Equivalent tonew CommandLine(command).usage(out, colorScheme).voidusage(PrintStream out)Delegates tousage(PrintStream, Help.ColorScheme)with the configured color scheme.voidusage(PrintStream out, CommandLine.Help.Ansi ansi)Delegates tousage(PrintStream, Help.ColorScheme)with the default color scheme.voidusage(PrintStream out, CommandLine.Help.ColorScheme colorScheme)Prints a usage help message for the annotated command class to the specifiedPrintStream.voidusage(PrintWriter writer)Delegates tousage(PrintWriter, Help.ColorScheme)with the configured color scheme.voidusage(PrintWriter writer, CommandLine.Help.Ansi ansi)Similar tousage(PrintStream, Help.Ansi)but with the specifiedPrintWriterinstead of aPrintStream.voidusage(PrintWriter writer, CommandLine.Help.ColorScheme colorScheme)Similar tousage(PrintStream, Help.ColorScheme), but with the specifiedPrintWriterinstead of aPrintStream.
-
-
-
Field Detail
-
VERSION
public static final String VERSION
This is picocli version "4.7.7".- See Also:
- Constant Field Values
-
-
Constructor Detail
-
CommandLine
public CommandLine(Object command)
Constructs a newCommandLineinterpreter with the specified object (which may be an annotated user object or aCommandSpec) and a default factory.The specified object may be a
CommandSpecobject, or it may be a@Command-annotated user object with@Optionand@Parameters-annotated fields and methods, in which case picocli automatically constructs aCommandSpecfrom this user object.If the specified command object is an interface
Classwith@Optionand@Parameters-annotated methods, picocli creates aProxywhose methods return the matched command line values. If the specified command object is a concreteClass, picocli delegates to the default factory to get an instance.If the specified object implements
RunnableorCallable, or if it is aMethodobject, the command can be run as an application in a single line of code by using theexecutemethod to omit some boilerplate code for handling help requests and invalid input. SeegetCommandMethodsfor a convenient way to obtain a commandMethod.When the
parseArgs(String...)method is called, theCommandSpecobject will be initialized based on command line arguments. If the commandSpec is created from an annotated user object, this user object will be initialized based on the command line arguments.- Parameters:
command- an annotated user object or aCommandSpecobject to initialize from the command line arguments- Throws:
CommandLine.InitializationException- if the specified command object does not have aCommandLine.Command,CommandLine.OptionorCommandLine.Parametersannotation
-
CommandLine
public CommandLine(Object command, CommandLine.IFactory factory)
Constructs a newCommandLineinterpreter with the specified object (which may be an annotated user object or aCommandSpec) and object factory.The specified object may be a
CommandSpecobject, or it may be a@Command-annotated user object with@Optionand@Parameters-annotated fields and methods, in which case picocli automatically constructs aCommandSpecfrom this user object.If the specified command object is an interface
Classwith@Optionand@Parameters-annotated methods, picocli creates aProxywhose methods return the matched command line values. If the specified command object is a concreteClass, picocli delegates to the factory to get an instance.If the specified object implements
RunnableorCallable, or if it is aMethodobject, the command can be run as an application in a single line of code by using theexecutemethod to omit some boilerplate code for handling help requests and invalid input. SeegetCommandMethodsfor a convenient way to obtain a commandMethod.When the
parseArgs(String...)method is called, theCommandSpecobject will be initialized based on command line arguments. If the commandSpec is created from an annotated user object, this user object will be initialized based on the command line arguments.- Parameters:
command- an annotated user object or aCommandSpecobject to initialize from the command line argumentsfactory- the factory used to create instances of subcommands, converters, etc., that are registered declaratively with annotation attributes- Throws:
CommandLine.InitializationException- if the specified command object does not have aCommandLine.Command,CommandLine.OptionorCommandLine.Parametersannotation- Since:
- 2.2
-
-
Method Detail
-
getCommandSpec
public CommandLine.Model.CommandSpec getCommandSpec()
Returns theCommandSpecmodel that thisCommandLinewas constructed with.- Returns:
- the
CommandSpecmodel - Since:
- 3.0
-
addMixin
public CommandLine addMixin(String name, Object mixin)
Adds the options and positional parameters in the specified mixin to this command.The specified object may be a
CommandSpecobject, or it may be a user object with@Optionand@Parameters-annotated fields, in which case picocli automatically constructs aCommandSpecfrom this user object.- Parameters:
name- the name by which the mixin object may later be retrievedmixin- an annotated user object or aCommandSpecobject whose options and positional parameters to add to this command- Returns:
- this CommandLine object, to allow method chaining
- Since:
- 3.0
-
getMixins
public Map<String,Object> getMixins()
Returns a map of user objects whose options and positional parameters were added to ("mixed in" with) this command.- Returns:
- a new Map containing the user objects mixed in with this command. If
CommandSpecobjects without user objects were programmatically added, use theunderlying modeldirectly. - Since:
- 3.0
-
addSubcommand
public CommandLine addSubcommand(Object command)
Registers a subcommand with the name obtained from the@Command(name = "...")annotation attribute of the specified command.- Parameters:
command- the object to initialize with command line arguments following the subcommand name. This may be aClassthat has a@Commandannotation, or an instance of such a class, or aCommandSpecorCommandLineinstance with its own (nested) subcommands.- Returns:
- this CommandLine object, to allow method chaining
- Throws:
CommandLine.InitializationException- if no name could be found for the specified subcommand, or if another subcommand was already registered under the same name, or if one of the aliases of the specified subcommand was already used by another subcommand.- Since:
- 4.0
- See Also:
addSubcommand(String, Object)
-
addSubcommand
public CommandLine addSubcommand(String name, Object command)
Registers a subcommand with the specified name. For example:CommandLine commandLine = new CommandLine(new Git()) .addSubcommand("status", new GitStatus()) .addSubcommand("commit", new GitCommit(); .addSubcommand("add", new GitAdd()) .addSubcommand("branch", new GitBranch()) .addSubcommand("checkout", new GitCheckout()) //... ;The specified object can be an annotated object or a
CommandLineinstance with its own nested subcommands. For example:CommandLine commandLine = new CommandLine(new MainCommand()) .addSubcommand("cmd1", new ChildCommand1()) // subcommand .addSubcommand("cmd2", new ChildCommand2()) .addSubcommand("cmd3", new CommandLine(new ChildCommand3()) // subcommand with nested sub-subcommands .addSubcommand("cmd3sub1", new GrandChild3Command1()) .addSubcommand("cmd3sub2", new GrandChild3Command2()) .addSubcommand("cmd3sub3", new CommandLine(new GrandChild3Command3()) // deeper nesting .addSubcommand("cmd3sub3sub1", new GreatGrandChild3Command3_1()) .addSubcommand("cmd3sub3sub2", new GreatGrandChild3Command3_2()) ) );The default type converters are available on all subcommands and nested sub-subcommands, but custom type converters are registered only with the subcommand hierarchy as it existed when the custom type was registered. To ensure a custom type converter is available to all subcommands, register the type converter last, after adding subcommands.
See also the
CommandLine.Command.subcommands()annotation to register subcommands declaratively.- Parameters:
name- the string to recognize on the command line as a subcommand. Ifnull, the name of the specified subcommand is used; if this is alsonull, the first alias is used.command- the object to initialize with command line arguments following the subcommand name. This may be aClassthat has a@Commandannotation, or an instance of such a class, or aCommandSpecorCommandLineinstance with its own (nested) subcommands.- Returns:
- this CommandLine object, to allow method chaining
- Throws:
CommandLine.InitializationException- if the specified name isnull, and no alternative name could be found, or if another subcommand was already registered under the same name, or if one of the aliases of the specified subcommand was already used by another subcommand.- Since:
- 0.9.7
- See Also:
registerConverter(Class, ITypeConverter),CommandLine.Command.subcommands()
-
addSubcommand
public CommandLine addSubcommand(String name, Object command, String... aliases)
Registers a subcommand with the specified name and all specified aliases. See alsoaddSubcommand(String, Object).- Parameters:
name- the string to recognize on the command line as a subcommand. Ifnull, the name of the specified subcommand is used; if this is alsonull, the first alias is used.command- the object to initialize with command line arguments following the subcommand name. This may be aClassthat has a@Commandannotation, or an instance of such a class, or aCommandSpecorCommandLineinstance with its own (nested) subcommands.aliases- zero or more alias names that are also recognized on the command line as this subcommand- Returns:
- this CommandLine object, to allow method chaining
- Throws:
CommandLine.InitializationException- if the specified name isnull, and no alternative name could be found, or if another subcommand was already registered under the same name, or if one of the aliases of the specified subcommand was already used by another subcommand.- Since:
- 3.1
- See Also:
addSubcommand(String, Object)
-
getSubcommands
public Map<String,CommandLine> getSubcommands()
Returns a map with the subcommands registered on this instance.- Returns:
- a map with the registered subcommands
- Since:
- 0.9.7
-
getParent
public CommandLine getParent()
Returns the command that this is a subcommand of, ornullif this is a top-level command.- Returns:
- the command that this is a subcommand of, or
nullif this is a top-level command - Since:
- 0.9.8
- See Also:
addSubcommand(String, Object),CommandLine.Command.subcommands()
-
getCommand
public <T> T getCommand()
Returns the annotated user object that thisCommandLineinstance was constructed with.- Type Parameters:
T- the type of the variable that the return value is being assigned to- Returns:
- the annotated object that this
CommandLineinstance was constructed with - Since:
- 0.9.7
-
getFactory
public CommandLine.IFactory getFactory()
Returns the factory that thisCommandLinewas constructed with.- Returns:
- the factory that this
CommandLinewas constructed with, nevernull - Since:
- 4.6
-
isUsageHelpRequested
public boolean isUsageHelpRequested()
Returnstrueif an option annotated withCommandLine.Option.usageHelp()was specified on the command line.- Returns:
- whether the parser encountered an option annotated with
CommandLine.Option.usageHelp(). - Since:
- 0.9.8
-
isVersionHelpRequested
public boolean isVersionHelpRequested()
Returnstrueif an option annotated withCommandLine.Option.versionHelp()was specified on the command line.- Returns:
- whether the parser encountered an option annotated with
CommandLine.Option.versionHelp(). - Since:
- 0.9.8
-
getHelp
public CommandLine.Help getHelp()
Returns a newHelpobject created by theIHelpFactorywith theCommandSpecandColorSchemeof this command.- Since:
- 4.1
- See Also:
Help#Help(CommandSpec, Help.ColorScheme),getHelpFactory(),getCommandSpec(),getColorScheme()
-
getHelpFactory
public CommandLine.IHelpFactory getHelpFactory()
Returns theIHelpFactorythat is used to construct the usage help message.- Since:
- 3.9
- See Also:
setHelpFactory(IHelpFactory)
-
setHelpFactory
public CommandLine setHelpFactory(CommandLine.IHelpFactory helpFactory)
Sets a newIHelpFactoryto customize the usage help message.The specified setting will be registered with this
CommandLineand the full hierarchy of its subcommands and nested sub-subcommands at the moment this method is called. Subcommands added later will have the default setting. To ensure a setting is applied to all subcommands, call the setter last, after adding subcommands.- Parameters:
helpFactory- the new help factory. Must be non-null.- Returns:
- this
CommandLineobject, to allow method chaining - Since:
- 3.9
-
getHelpSectionKeys
public List<String> getHelpSectionKeys()
Returns the section keys in the order that the usage help message should render the sections. This ordering may be modified withsetSectionKeys. The default keys are (in order):SECTION_KEY_HEADER_HEADINGSECTION_KEY_HEADERSECTION_KEY_SYNOPSIS_HEADINGSECTION_KEY_SYNOPSISSECTION_KEY_DESCRIPTION_HEADINGSECTION_KEY_DESCRIPTIONSECTION_KEY_PARAMETER_LIST_HEADINGSECTION_KEY_AT_FILE_PARAMETERSECTION_KEY_PARAMETER_LISTSECTION_KEY_OPTION_LIST_HEADINGSECTION_KEY_OPTION_LISTSECTION_KEY_COMMAND_LIST_HEADINGSECTION_KEY_COMMAND_LISTSECTION_KEY_EXIT_CODE_LIST_HEADINGSECTION_KEY_EXIT_CODE_LISTSECTION_KEY_FOOTER_HEADINGSECTION_KEY_FOOTER
- Since:
- 3.9
-
setHelpSectionKeys
public CommandLine setHelpSectionKeys(List<String> keys)
Sets the section keys in the order that the usage help message should render the sections.The specified setting will be registered with this
CommandLineand the full hierarchy of its subcommands and nested sub-subcommands at the moment this method is called. Subcommands added later will have the default setting. To ensure a setting is applied to all subcommands, call the setter last, after adding subcommands.Use
CommandLine.Model.UsageMessageSpec.sectionKeys(List)to customize a command without affecting its subcommands.- Since:
- 3.9
- See Also:
getHelpSectionKeys()
-
getHelpSectionMap
public Map<String,CommandLine.IHelpSectionRenderer> getHelpSectionMap()
Returns the map of section keys and renderers used to construct the usage help message. The usage help message can be customized by adding, replacing and removing section renderers from this map. Sections can be reordered withsetSectionKeys. Sections that are either not in this map or not in the list returned bygetSectionKeysare omitted.NOTE: By modifying the returned
Map, only the usage help message of this command is affected. UsesetHelpSectionMap(Map)to customize the usage help message for this command and all subcommands.- Since:
- 3.9
-
setHelpSectionMap
public CommandLine setHelpSectionMap(Map<String,CommandLine.IHelpSectionRenderer> map)
Sets the map of section keys and renderers used to construct the usage help message.The specified setting will be registered with this
CommandLineand the full hierarchy of its subcommands and nested sub-subcommands at the moment this method is called. Subcommands added later will have the default setting. To ensure a setting is applied to all subcommands, call the setter last, after adding subcommands.Use
CommandLine.Model.UsageMessageSpec.sectionMap(Map)to customize a command without affecting its subcommands.- Since:
- 3.9
- See Also:
getHelpSectionMap()
-
isAdjustLineBreaksForWideCJKCharacters
public boolean isAdjustLineBreaksForWideCJKCharacters()
Returns whether line breaks should take wide Chinese, Japanese and Korean characters into account for line-breaking purposes. The default istrue.- Returns:
- true if wide Chinese, Japanese and Korean characters are counted as double the size of other characters for line-breaking purposes
- Since:
- 4.0
-
setAdjustLineBreaksForWideCJKCharacters
public CommandLine setAdjustLineBreaksForWideCJKCharacters(boolean adjustForWideChars)
Sets whether line breaks should take wide Chinese, Japanese and Korean characters into account, and returns this UsageMessageSpec. The default istrue.The specified setting will be registered with this
CommandLineand the full hierarchy of its subcommands and nested sub-subcommands at the moment this method is called. Subcommands added later will have the default setting. To ensure a setting is applied to all subcommands, call the setter last, after adding subcommands.- Parameters:
adjustForWideChars- if true, wide Chinese, Japanese and Korean characters are counted as double the size of other characters for line-breaking purposes- Since:
- 4.0
-
isToggleBooleanFlags
public boolean isToggleBooleanFlags()
Returns whether the value of boolean flag options should be "toggled" when the option is matched. From 4.0, this isfalseby default, and when a flag option is specified on the command line picocli will set its value to the opposite of its default value. If this method returnstrue, flags are toggled, so if the value istrueit is set tofalse, and when the value isfalseit is set totrue. When toggling is enabled, specifying a flag option twice on the command line will have no effect because they cancel each other out.- Returns:
truethe value of boolean flag options should be "toggled" when the option is matched,falseotherwise- Since:
- 3.0
-
setToggleBooleanFlags
public CommandLine setToggleBooleanFlags(boolean newValue)
Sets whether the value of boolean flag options should be "toggled" when the option is matched. The default isfalse, and when a flag option is specified on the command line picocli will set its value to the opposite of its default value.The specified setting will be registered with this
CommandLineand the full hierarchy of its subcommands and nested sub-subcommands at the moment this method is called. Subcommands added later will have the default setting. To ensure a setting is applied to all subcommands, call the setter last, after adding subcommands.- Parameters:
newValue- the new setting- Returns:
- this
CommandLineobject, to allow method chaining - Since:
- 3.0
-
isInterpolateVariables
public boolean isInterpolateVariables()
Returns whether variables should be interpolated in String values. The default istrue.- Since:
- 4.0
-
setInterpolateVariables
public CommandLine setInterpolateVariables(boolean interpolate)
Sets whether variables should be interpolated in String values. The default istrue.The specified setting will be registered with this
CommandLineand the full hierarchy of its subcommands and nested sub-subcommands at the moment this method is called. Subcommands added later will have the default setting. To ensure a setting is applied to all subcommands, call the setter last, after adding subcommands.- Since:
- 4.0
-
isOverwrittenOptionsAllowed
public boolean isOverwrittenOptionsAllowed()
Returns whether options for single-value fields can be specified multiple times on the command line. The default isfalseand aCommandLine.OverwrittenOptionExceptionis thrown if this happens. Whentrue, the last specified value is retained.- Returns:
trueif options for single-value fields can be specified multiple times on the command line,falseotherwise- Since:
- 0.9.7
-
setOverwrittenOptionsAllowed
public CommandLine setOverwrittenOptionsAllowed(boolean newValue)
Sets whether options for single-value fields can be specified multiple times on the command line without aCommandLine.OverwrittenOptionExceptionbeing thrown. The default isfalse.The specified setting will be registered with this
CommandLineand the full hierarchy of its subcommands and nested sub-subcommands at the moment this method is called. Subcommands added later will have the default setting. To ensure a setting is applied to all subcommands, call the setter last, after adding subcommands.- Parameters:
newValue- the new setting- Returns:
- this
CommandLineobject, to allow method chaining - Since:
- 0.9.7
-
isPosixClusteredShortOptionsAllowed
public boolean isPosixClusteredShortOptionsAllowed()
Returns whether the parser accepts clustered short options. The default istrue.- Returns:
trueif short options like-x -v -f SomeFilecan be clustered together like-xvfSomeFile,falseotherwise- Since:
- 3.0
-
setPosixClusteredShortOptionsAllowed
public CommandLine setPosixClusteredShortOptionsAllowed(boolean newValue)
Sets whether short options like-x -v -f SomeFilecan be clustered together like-xvfSomeFile. The default istrue.The specified setting will be registered with this
CommandLineand the full hierarchy of its subcommands and nested sub-subcommands at the moment this method is called. Subcommands added later will have the default setting. To ensure a setting is applied to all subcommands, call the setter last, after adding subcommands.- Parameters:
newValue- the new setting- Returns:
- this
CommandLineobject, to allow method chaining - Since:
- 3.0
-
isCaseInsensitiveEnumValuesAllowed
public boolean isCaseInsensitiveEnumValuesAllowed()
Returns whether the parser should ignore case when converting arguments toenumvalues. The default isfalse.- Returns:
trueif enum values can be specified that don't match thetoString()value of the enum constant,falseotherwise; e.g., for an option of type java.time.DayOfWeek, valuesMonDaY,mondayandMONDAYare all recognized iftrue.- Since:
- 3.4
-
setCaseInsensitiveEnumValuesAllowed
public CommandLine setCaseInsensitiveEnumValuesAllowed(boolean newValue)
Sets whether the parser should ignore case when converting arguments toenumvalues. The default isfalse. When set to true, for example, for an option of type java.time.DayOfWeek, valuesMonDaY,mondayandMONDAYare all recognized iftrue.The specified setting will be registered with this
CommandLineand the full hierarchy of its subcommands and nested sub-subcommands at the moment this method is called. Subcommands added later will have the default setting. To ensure a setting is applied to all subcommands, call the setter last, after adding subcommands.- Parameters:
newValue- the new setting- Returns:
- this
CommandLineobject, to allow method chaining - Since:
- 3.4
-
isTrimQuotes
public boolean isTrimQuotes()
Returns whether the parser should trim quotes from command line arguments. The default is read from the system property "picocli.trimQuotes" and will betrueif the property is present and empty, or if its value is "true".If this property is set to
true, the parser will remove quotes from the command line arguments, as follows:- if the command line argument contains just the leading and trailing quote, these quotes are removed
- if the command line argument contains more quotes than just the leading and trailing quote, the parser first
tries to process the parameter with the quotes intact. For example, the
splitregular expression inside a quoted region should be ignored, so arguments like"a,b","x,y"are handled correctly. For arguments with nested quotes, quotes are removed later in the processing pipeline, aftersplitoperations are applied.
- Returns:
trueif the parser should trim quotes from command line arguments before processing them,falseotherwise;- Since:
- 3.7
- See Also:
CommandLine.Model.ParserSpec.trimQuotes()
-
setTrimQuotes
public CommandLine setTrimQuotes(boolean newValue)
Sets whether the parser should trim quotes from command line arguments before processing them. The default is read from the system property "picocli.trimQuotes" and will betrueif the property is set and empty, or if its value is "true".If this property is set to
true, the parser will remove quotes from the command line arguments, as follows:- if the command line argument contains just the leading and trailing quote, these quotes are removed
- if the command line argument contains more quotes than just the leading and trailing quote, the parser first
tries to process the parameter with the quotes intact. For example, the
splitregular expression inside a quoted region should be ignored, so arguments like"a,b","x,y"are handled correctly. For arguments with nested quotes, quotes are removed later in the processing pipeline, aftersplitoperations are applied.
The specified setting will be registered with this
CommandLineand the full hierarchy of its subcommands and nested sub-subcommands at the moment this method is called. Subcommands added later will have the default setting. To ensure a setting is applied to all subcommands, call the setter last, after adding subcommands.Calling this method will cause the "picocli.trimQuotes" property to have no effect.
- Parameters:
newValue- the new setting- Returns:
- this
CommandLineobject, to allow method chaining - Since:
- 3.7
- See Also:
CommandLine.Model.ParserSpec.trimQuotes(boolean)
-
isSplitQuotedStrings
@Deprecated public boolean isSplitQuotedStrings()
Deprecated. Most applications should not change the default. The rare application that does need to split parameter values without respecting quotes should useCommandLine.Model.ParserSpec.splitQuotedStrings(boolean).Returns whether the parser is allowed to split quoted Strings or not. The default isfalse, so quotes are respected: quoted strings are treated as a single value that should not be broken up.For example, take a single command line parameter
"a,b","x,y". With a comma split regex, the default ofsplitQuotedStrings = falsemeans that this value will be split into two strings:"a,b"and"x,y". This is usually what you want.If
splitQuotedStringsis set totrue, quotes are not respected, and the value is split up into four parts: the first is"a, the second isb", the third is"x, and the last part isy". This is generally not what you want.- Returns:
trueif the parser is allowed to split quoted Strings,falseotherwise;- Since:
- 3.7
- See Also:
CommandLine.Model.ArgSpec.splitRegex(),CommandLine.Model.ParserSpec.splitQuotedStrings()
-
setSplitQuotedStrings
@Deprecated public CommandLine setSplitQuotedStrings(boolean newValue)
Deprecated. Most applications should not change the default. The rare application that does need to split parameter values without respecting quotes should useCommandLine.Model.ParserSpec.splitQuotedStrings(boolean).Sets whether the parser is allowed to split quoted Strings. The default isfalse, so quotes are respected: quoted strings are treated as a single value that should not be broken up.For example, take a single command line parameter
"a,b","x,y". With a comma split regex, the default ofsplitQuotedStrings = falsemeans that this value will be split into two strings:"a,b"and"x,y". This is usually what you want.However, if
splitQuotedStringsis set totrue, quotes are not respected, and the value is split up into four parts: the first is"a, the second isb", the third is"x, and the last part isy". This is generally not what you want.The specified setting will be registered with this
CommandLineand the full hierarchy of its subcommands and nested sub-subcommands at the moment this method is called. Subcommands added later will have the default setting. To ensure a setting is applied to all subcommands, call the setter last, after adding subcommands.- Parameters:
newValue- the new setting- Returns:
- this
CommandLineobject, to allow method chaining - Since:
- 3.7
- See Also:
CommandLine.Model.ArgSpec.splitRegex(),CommandLine.Model.ParserSpec.splitQuotedStrings(boolean)
-
getEndOfOptionsDelimiter
public String getEndOfOptionsDelimiter()
Returns the end-of-options delimiter that signals that the remaining command line arguments should be treated as positional parameters.- Returns:
- the end-of-options delimiter. The default is
"--". - Since:
- 3.5
-
setEndOfOptionsDelimiter
public CommandLine setEndOfOptionsDelimiter(String delimiter)
Sets the end-of-options delimiter that signals that the remaining command line arguments should be treated as positional parameters.- Parameters:
delimiter- the end-of-options delimiter; must not benull. The default is"--".- Returns:
- this
CommandLineobject, to allow method chaining - Since:
- 3.5
-
isSubcommandsCaseInsensitive
public boolean isSubcommandsCaseInsensitive()
Returns whether upper case and lower case should be ignored when matching subcommands. The default isfalse.- Returns:
trueif subcommands can be matched when they differ only in case from thegetCommandName()value of a registered one,falseotherwise. For example, if true, for a subcommand with namehelp, inputs likehelp,HeLpandHELPare all recognized.- Since:
- 4.3
-
setSubcommandsCaseInsensitive
public CommandLine setSubcommandsCaseInsensitive(boolean newValue)
Sets whether upper case and lower case should be ignored when matching subcommands. The default isfalse. For example, when set totrue, for a subcommand with namehelp, inputs likehelp,HeLpandHELPare all recognized.The specified setting will be registered with this
CommandLineand the full hierarchy of its subcommands and nested sub-subcommands at the moment this method is called. Subcommands added later will have the default setting. To ensure a setting is applied to all subcommands, call the setter last, after adding subcommands.- Parameters:
newValue- the new setting- Returns:
- this
CommandLineobject, to allow method chaining - Since:
- 4.3
-
isOptionsCaseInsensitive
public boolean isOptionsCaseInsensitive()
Returns whether upper case and lower case should be ignored when matching option names. The default isfalse.- Returns:
trueif options can be matched when they differ only in case from thenames()value of a registered one,falseotherwise; For example, if true, for an option with name-h, inputs like-h,-Hare both recognized.- Since:
- 4.3
-
setOptionsCaseInsensitive
public CommandLine setOptionsCaseInsensitive(boolean newValue)
Sets whether upper case and lower case should be ignored when matching option names. The default isfalse. For example, when set totrue, for an option with name-h, inputs like-h,-Hare both recognized.The specified setting will be registered with this
Note that changing case sensitivity will also change the case sensitivity of negatable options: any customCommandLineand the full hierarchy of its subcommands and nested sub-subcommands at the moment this method is called. Subcommands added later will have the default setting. To ensure a setting is applied to all subcommands, call the setter last, after adding subcommands.CommandLine.INegatableOptionTransformerthat was previously installed will be replaced by the case-insensitive version of the default transformer. To ensure your custom transformer is used, install it last, after changing case sensitivity.- Parameters:
newValue- the new setting- Returns:
- this
CommandLineobject, to allow method chaining - Since:
- 4.3
-
isAbbreviatedSubcommandsAllowed
public boolean isAbbreviatedSubcommandsAllowed()
Returns whether abbreviation of subcommands should be allowed when matching subcommands. The default isfalse.- Returns:
trueif subcommands can be matched when they are abbreviations of thegetCommandName()value of a registered one,falseotherwise. For example, if true, for a subcommand with namehelpCommand, inputs likeh,h-candhCare all recognized.- Since:
- 4.4
-
setAbbreviatedSubcommandsAllowed
public CommandLine setAbbreviatedSubcommandsAllowed(boolean newValue)
Sets whether abbreviated subcommands should be matched. The default isfalse. For example, when set totrue, for a subcommandhelpCommand, inputs likeh,h-candhCare all recognized.The specified setting will be registered with this
CommandLineand the full hierarchy of its subcommands and nested sub-subcommands at the moment this method is called. Subcommands added later will have the default setting. To ensure a setting is applied to all subcommands, call the setter last, after adding subcommands.- Parameters:
newValue- the new setting- Returns:
- this
CommandLineobject, to allow method chaining - Since:
- 4.4
-
isAbbreviatedOptionsAllowed
public boolean isAbbreviatedOptionsAllowed()
Returns whether abbreviation of option names should be allowed when matching options. The default isfalse.- Returns:
trueif options can be matched when they are abbreviations of thenames()value of a registered one,falseotherwise. For example, if true, for a subcommand with name--helpMe, inputs like--h,--h-mand--hMare all recognized.- Since:
- 4.4
-
setAbbreviatedOptionsAllowed
public CommandLine setAbbreviatedOptionsAllowed(boolean newValue)
Sets whether abbreviated option names should be matched. The default isfalse. For example, when set totrue, for an option with name--helpMe, inputs like--h,--h-mand--hMare all recognized.The specified setting will be registered with this
CommandLineand the full hierarchy of its subcommands and nested sub-subcommands at the moment this method is called. Subcommands added later will have the default setting. To ensure a setting is applied to all subcommands, call the setter last, after adding subcommands.- Parameters:
newValue- the new setting- Returns:
- this
CommandLineobject, to allow method chaining - Since:
- 4.4
-
getDefaultValueProvider
public CommandLine.IDefaultValueProvider getDefaultValueProvider()
Returns the default value provider for the command, ornullif none has been set.- Returns:
- the default value provider for this command, or
null - Since:
- 3.6
- See Also:
CommandLine.Command.defaultValueProvider(),CommandLine.Model.CommandSpec.defaultValueProvider(),CommandLine.Model.ArgSpec.defaultValueString()
-
setDefaultValueProvider
public CommandLine setDefaultValueProvider(CommandLine.IDefaultValueProvider newValue)
Sets a default value provider for the command and sub-commandsThe specified setting will be registered with this
CommandLineand the full hierarchy of its sub-commands and nested sub-subcommands at the moment this method is called. Sub-commands added later will have the default setting. To ensure a setting is applied to all sub-commands, call the setter last, after adding sub-commands.- Parameters:
newValue- the default value provider to use- Returns:
- this
CommandLineobject, to allow method chaining - Since:
- 3.6
-
isStopAtPositional
public boolean isStopAtPositional()
Returns whether the parser interprets the first positional parameter as "end of options" so the remaining arguments are all treated as positional parameters. The default isfalse.- Returns:
trueif all values following the first positional parameter should be treated as positional parameters,falseotherwise- Since:
- 2.3
-
setStopAtPositional
public CommandLine setStopAtPositional(boolean newValue)
Sets whether the parser interprets the first positional parameter as "end of options" so the remaining arguments are all treated as positional parameters. The default isfalse.The specified setting will be registered with this
CommandLineand the full hierarchy of its subcommands and nested sub-subcommands at the moment this method is called. Subcommands added later will have the default setting. To ensure a setting is applied to all subcommands, call the setter last, after adding subcommands.- Parameters:
newValue-trueif all values following the first positional parameter should be treated as positional parameters,falseotherwise- Returns:
- this
CommandLineobject, to allow method chaining - Since:
- 2.3
-
isStopAtUnmatched
public boolean isStopAtUnmatched()
Returns whether the parser should stop interpreting options and positional parameters as soon as it encounters an unmatched option. Unmatched options are arguments that look like an option but are not one of the known options, or positional arguments for which there is no available slots (the command has no positional parameters or their size is limited). The default isfalse.Setting this flag to
trueautomatically sets the unmatchedArgumentsAllowed flag totruealso.- Returns:
truewhen an unmatched option should result in the remaining command line arguments to be added to the unmatchedArguments list- Since:
- 2.3
-
setStopAtUnmatched
public CommandLine setStopAtUnmatched(boolean newValue)
Sets whether the parser should stop interpreting options and positional parameters as soon as it encounters an unmatched option. Unmatched options are arguments that look like an option but are not one of the known options, or positional arguments for which there is no available slots (the command has no positional parameters or their size is limited). The default isfalse.Setting this flag to
trueautomatically sets the unmatchedArgumentsAllowed flag totruealso.The specified setting will be registered with this
CommandLineand the full hierarchy of its subcommands and nested sub-subcommands at the moment this method is called. Subcommands added later will have the default setting. To ensure a setting is applied to all subcommands, call the setter last, after adding subcommands.- Parameters:
newValue-truewhen an unmatched option should result in the remaining command line arguments to be added to the unmatchedArguments list- Returns:
- this
CommandLineobject, to allow method chaining - Since:
- 2.3
-
isAllowSubcommandsAsOptionParameters
public boolean isAllowSubcommandsAsOptionParameters()
Returns whether options can have parameter values that match subcommand names or aliases, or whether such values should be rejected with a missing parameter exception. The default isfalse, so by default input like-x=subcommandis rejected if-xis an option that takes a String parameter, andsubcommandis a subcommand of this command.- Returns:
truewhen options can have parameter values that match subcommand names or aliases,falsewhen such values should be rejected with a missing parameter exception- Since:
- 4.7.7
- See Also:
CommandLine.Model.ParserSpec.allowSubcommandsAsOptionParameters()
-
setAllowSubcommandsAsOptionParameters
public CommandLine setAllowSubcommandsAsOptionParameters(boolean newValue)
Sets whether options can have parameter values that match subcommand names or aliases, or whether such values should be rejected with a missing parameter exception. The default isfalse, so by default input like-x=subcommandis rejected if-xis an option that takes a String parameter, andsubcommandis a subcommand of this command.The specified setting will be registered with this
CommandLineand the full hierarchy of its subcommands and nested sub-subcommands at the moment this method is called. Subcommands added later will have the default setting. To ensure a setting is applied to all subcommands, call the setter last, after adding subcommands.- Parameters:
newValue- the new setting. Whentrue, options can have parameter values that match subcommand names or aliases, whenfalse, such values are rejected with a missing parameter exception- Returns:
- this
CommandLineobject, to allow method chaining - Since:
- 4.7.7
- See Also:
CommandLine.Model.ParserSpec.allowSubcommandsAsOptionParameters(boolean)
-
isAllowOptionsAsOptionParameters
public boolean isAllowOptionsAsOptionParameters()
Returns whether options can have parameter values that match the name of an option in this command, or whether such values should be rejected with a missing parameter exception. The default isfalse, so by default input like-x=--some-optionis rejected if-xis an option that takes a String parameter, and--some-optionis an option of this command.This method only considers actual options of this command, as opposed to
isUnmatchedOptionsAllowedAsOptionParameters(), which considers values that resemble options.- Returns:
truewhen options can have parameter values that match the name of an option in this command,falsewhen such values should be rejected with a missing parameter exception- Since:
- 4.7.7
- See Also:
isUnmatchedOptionsAllowedAsOptionParameters(),CommandLine.Model.ParserSpec.allowOptionsAsOptionParameters()
-
setAllowOptionsAsOptionParameters
public CommandLine setAllowOptionsAsOptionParameters(boolean newValue)
Sets whether options can have parameter values that match the name of an option in this command, or whether such values should be rejected with a missing parameter exception. The default isfalse, so by default input like-x=--some-optionis rejected if-xis an option that takes a String parameter, and--some-optionis an option of this command.This method only considers actual options of this command, as opposed to
setUnmatchedOptionsAllowedAsOptionParameters(boolean), which considers values that resemble options.Use with caution! When set to
true, any option in the command will consume the maximum number of arguments possible for its arity. This means that an option witharity = "*"will consume all command line arguments following that option. If this is not what you want, consider custom parameter processing.The specified setting will be registered with this
CommandLineand the full hierarchy of its subcommands and nested sub-subcommands at the moment this method is called. Subcommands added later will have the default setting. To ensure a setting is applied to all subcommands, call the setter last, after adding subcommands.- Parameters:
newValue- the new setting. Whentrue, options can have parameter values that match the name of an option in this command, whenfalse, such values are rejected with a missing parameter exception- Returns:
- this
CommandLineobject, to allow method chaining - Since:
- 4.7.7
- See Also:
setUnmatchedOptionsAllowedAsOptionParameters(boolean),CommandLine.Model.ParserSpec.allowOptionsAsOptionParameters(boolean)
-
isUnmatchedOptionsAllowedAsOptionParameters
public boolean isUnmatchedOptionsAllowedAsOptionParameters()
Returns whether options can have parameter values that resemble an option, or whether such values should be rejected as unknown options. The default istrue, so by default input like-x=-unknownis accepted if-xis an option that takes a String parameter.This method only considers values that resemble options, as opposed to
isAllowOptionsAsOptionParameters(), which considers actual options of this command.- Returns:
truewhen options can have parameter values that resemble an option,falsewhen such values should be rejected as unknown options- Since:
- 4.4
- See Also:
isAllowOptionsAsOptionParameters(),CommandLine.Model.ParserSpec.unmatchedOptionsAllowedAsOptionParameters()
-
setUnmatchedOptionsAllowedAsOptionParameters
public CommandLine setUnmatchedOptionsAllowedAsOptionParameters(boolean newValue)
Sets whether options can have parameter values that resemble an option, or whether such values should be rejected as unknown options. The default istrue, so by default input like-x=-unknownis accepted if-xis an option that takes a String parameter.This method only considers values that resemble options, as opposed to
setAllowOptionsAsOptionParameters(boolean), which considers actual options of this command.The specified setting will be registered with this
CommandLineand the full hierarchy of its subcommands and nested sub-subcommands at the moment this method is called. Subcommands added later will have the default setting. To ensure a setting is applied to all subcommands, call the setter last, after adding subcommands.- Parameters:
newValue- the new setting. Whentrue, options can have parameter values that resemble an option, whenfalse, such values are rejected as unknown options- Returns:
- this
CommandLineobject, to allow method chaining - Since:
- 4.4
- See Also:
setAllowOptionsAsOptionParameters(boolean),CommandLine.Model.ParserSpec.unmatchedOptionsAllowedAsOptionParameters(boolean)
-
isUnmatchedOptionsArePositionalParams
public boolean isUnmatchedOptionsArePositionalParams()
Returns whether arguments on the command line that resemble an option should be treated as positional parameters. The default isfalseand the parser behaviour depends onisUnmatchedArgumentsAllowed().- Returns:
truearguments on the command line that resemble an option should be treated as positional parameters,falseotherwise- Since:
- 3.0
- See Also:
getUnmatchedArguments()
-
setUnmatchedOptionsArePositionalParams
public CommandLine setUnmatchedOptionsArePositionalParams(boolean newValue)
Sets whether arguments on the command line that resemble an option should be treated as positional parameters. The default isfalse.The specified setting will be registered with this
CommandLineand the full hierarchy of its subcommands and nested sub-subcommands at the moment this method is called. Subcommands added later will have the default setting. To ensure a setting is applied to all subcommands, call the setter last, after adding subcommands.- Parameters:
newValue- the new setting. Whentrue, arguments on the command line that resemble an option should be treated as positional parameters.- Returns:
- this
CommandLineobject, to allow method chaining - Since:
- 3.0
- See Also:
getUnmatchedArguments(),isUnmatchedArgumentsAllowed()
-
isUnmatchedArgumentsAllowed
public boolean isUnmatchedArgumentsAllowed()
Returns whether the end user may specify arguments on the command line that are not matched to any option or parameter fields. The default isfalseand aCommandLine.UnmatchedArgumentExceptionis thrown if this happens. Whentrue, the last unmatched arguments are available via thegetUnmatchedArguments()method.- Returns:
trueif the end use may specify unmatched arguments on the command line,falseotherwise- Since:
- 0.9.7
- See Also:
getUnmatchedArguments()
-
setUnmatchedArgumentsAllowed
public CommandLine setUnmatchedArgumentsAllowed(boolean newValue)
Sets whether the end user may specify unmatched arguments on the command line without aCommandLine.UnmatchedArgumentExceptionbeing thrown. The default isfalse.The specified setting will be registered with this
CommandLineand the full hierarchy of its subcommands and nested sub-subcommands at the moment this method is called. Subcommands added later will have the default setting. To ensure a setting is applied to all subcommands, call the setter last, after adding subcommands.- Parameters:
newValue- the new setting. Whentrue, the last unmatched arguments are available via thegetUnmatchedArguments()method.- Returns:
- this
CommandLineobject, to allow method chaining - Since:
- 0.9.7
- See Also:
getUnmatchedArguments()
-
getUnmatchedArguments
public List<String> getUnmatchedArguments()
Returns the list of unmatched command line arguments, if any.- Returns:
- the list of unmatched command line arguments or an empty list
- Since:
- 0.9.7
- See Also:
isUnmatchedArgumentsAllowed()
-
getColorScheme
public CommandLine.Help.ColorScheme getColorScheme()
Returns the color scheme to use when printing help. The default value is the default color scheme withAnsi.AUTO.
-
setColorScheme
public CommandLine setColorScheme(CommandLine.Help.ColorScheme colorScheme)
Sets the color scheme to use when printing help.The specified setting will be registered with this
CommandLineand the full hierarchy of its subcommands and nested sub-subcommands at the moment this method is called. Subcommands added later will have the default setting. To ensure a setting is applied to all subcommands, call the setter last, after adding subcommands.- Parameters:
colorScheme- the new color scheme- Since:
- 4.0
- See Also:
execute(String...),usage(PrintStream),usage(PrintWriter),getUsageMessage()
-
getOut
public PrintWriter getOut()
Returns the writer used when printing user-requested usage help or version help during command execution. Defaults to a PrintWriter wrapper aroundSystem.outunlesssetOut(PrintWriter)was called with a different writer.This method is used by
execute(String...). CustomIExecutionStrategyimplementations should also use this writer.By convention, when the user requests help with a
--helpor similar option, the usage help message is printed to the standard output stream so that it can be easily searched and paged.- Since:
- 4.0
-
setOut
public CommandLine setOut(PrintWriter out)
Sets the writer to use when printing user-requested usage help or version help during command execution.This method is used by
execute(String...). CustomIExecutionStrategyimplementations should also use this writer.The specified setting will be registered with this
CommandLineand the full hierarchy of its subcommands and nested sub-subcommands at the moment this method is called. Subcommands added later will have the default setting. To ensure a setting is applied to all subcommands, call the setter last, after adding subcommands.- Parameters:
out- the new PrintWriter to use- Returns:
- this CommandLine for method chaining
- Since:
- 4.0
-
getErr
public PrintWriter getErr()
Returns the writer to use when printing diagnostic (error) messages during command execution. Defaults to a PrintWriter wrapper aroundSystem.err, unlesssetErr(PrintWriter)was called with a different writer.This method is used by
execute(String...).IParameterExceptionHandlerandIExecutionExceptionHandlerimplementations should use this writer to print error messages (which may include a usage help message) when an unexpected error occurs.- Since:
- 4.0
-
setErr
public CommandLine setErr(PrintWriter err)
Sets the writer to use when printing diagnostic (error) messages during command execution.This method is used by
execute(String...).IParameterExceptionHandlerandIExecutionExceptionHandlerimplementations should use this writer to print error messages (which may include a usage help message) when an unexpected error occurs.The specified setting will be registered with this
CommandLineand the full hierarchy of its subcommands and nested sub-subcommands at the moment this method is called. Subcommands added later will have the default setting. To ensure a setting is applied to all subcommands, call the setter last, after adding subcommands.- Parameters:
err- the new PrintWriter to use- Returns:
- this CommandLine for method chaining
- Since:
- 4.0
-
getExitCodeExceptionMapper
public CommandLine.IExitCodeExceptionMapper getExitCodeExceptionMapper()
Returns the mapper that was set by the application to map from exceptions to exit codes, for use by theexecutemethod.- Returns:
- the mapper that was set, or
nullif none was set - Since:
- 4.0
-
setExitCodeExceptionMapper
public CommandLine setExitCodeExceptionMapper(CommandLine.IExitCodeExceptionMapper exitCodeExceptionMapper)
Sets the mapper used by theexecutemethod to map exceptions to exit codes.The specified setting will be registered with this
CommandLineand the full hierarchy of its subcommands and nested sub-subcommands at the moment this method is called. Subcommands added later will have the default setting. To ensure a setting is applied to all subcommands, call the setter last, after adding subcommands.- Parameters:
exitCodeExceptionMapper- the new value- Returns:
- this CommandLine for method chaining
- Since:
- 4.0
-
getExecutionStrategy
public CommandLine.IExecutionStrategy getExecutionStrategy()
Returns the execution strategy used by theexecutemethod to invoke the business logic on the user objects of this command and/or the user-specified subcommand(s). The default value isRunLast.- Returns:
- the execution strategy to run the user-specified command
- Since:
- 4.0
-
setExecutionStrategy
public CommandLine setExecutionStrategy(CommandLine.IExecutionStrategy executionStrategy)
Sets the execution strategy that theexecutemethod should use to invoke the business logic on the user objects of this command and/or the user-specified subcommand(s).The specified setting will be registered with this
CommandLineand the full hierarchy of its subcommands and nested sub-subcommands at the moment this method is called. Subcommands added later will have the default setting. To ensure a setting is applied to all subcommands, call the setter last, after adding subcommands.- Parameters:
executionStrategy- the new execution strategy to run the user-specified command- Returns:
- this CommandLine for method chaining
- Since:
- 4.0
-
getParameterExceptionHandler
public CommandLine.IParameterExceptionHandler getParameterExceptionHandler()
Returns the handler for dealing with invalid user input when the command is executed.The default implementation prints an error message describing the problem, followed by either suggested alternatives for mistyped options, or the full usage help message of the problematic command; it then delegates to the exit code exception mapper for an exit code, with
exitCodeOnInvalidInputas the default exit code.Alternatively, you can install a "short error message handler" like this:
static class ShortErrorMessageHandler implements IParameterExceptionHandler { public int handleParseException(ParameterException ex, String[] args) { CommandLine cmd = ex.getCommandLine(); PrintWriter writer = cmd.getErr(); writer.println(ex.getMessage()); UnmatchedArgumentException.printSuggestions(ex, writer); writer.print(cmd.getHelp().fullSynopsis()); CommandSpec spec = cmd.getCommandSpec(); writer.printf("Try '%s --help' for more information.%n", spec.qualifiedName()); return cmd.getExitCodeExceptionMapper() != null ? cmd.getExitCodeExceptionMapper().getExitCode(ex) : spec.exitCodeOnInvalidInput(); } }Install this error handler like this:
new CommandLine(new MyApp()) .setParameterExceptionHandler(new ShortErrorMessageHandler()) .execute(args);- Returns:
- the handler for dealing with invalid user input
- Since:
- 4.0
-
setParameterExceptionHandler
public CommandLine setParameterExceptionHandler(CommandLine.IParameterExceptionHandler parameterExceptionHandler)
Sets the handler for dealing with invalid user input when the command is executed.The specified setting will be registered with this
CommandLineand the full hierarchy of its subcommands and nested sub-subcommands at the moment this method is called. Subcommands added later will have the default setting. To ensure a setting is applied to all subcommands, call the setter last, after adding subcommands.- Parameters:
parameterExceptionHandler- the new handler for dealing with invalid user input- Returns:
- this CommandLine for method chaining
- Since:
- 4.0
- See Also:
an example short exception handler
-
getExecutionExceptionHandler
public CommandLine.IExecutionExceptionHandler getExecutionExceptionHandler()
Returns the handler for dealing with exceptions that occurred in theCallable,RunnableorMethoduser object of a command when the command was executed.The default implementation rethrows the specified exception.
- Returns:
- the handler for dealing with exceptions that occurred in the business logic when the
executemethod was invoked. - Since:
- 4.0
-
setExecutionExceptionHandler
public CommandLine setExecutionExceptionHandler(CommandLine.IExecutionExceptionHandler executionExceptionHandler)
Sets a custom handler for dealing with exceptions that occurred in theCallable,RunnableorMethoduser object of a command when the command was executed via the execute method.The specified setting will be registered with this
CommandLineand the full hierarchy of its subcommands and nested sub-subcommands at the moment this method is called. Subcommands added later will have the default setting. To ensure a setting is applied to all subcommands, call the setter last, after adding subcommands.- Parameters:
executionExceptionHandler- the handler for dealing with exceptions that occurred in the business logic when theexecutemethod was invoked.- Returns:
- this CommandLine for method chaining
- Since:
- 4.0
-
populateCommand
public static <T> T populateCommand(T command, String... args)Convenience method that initializes the specified annotated object from the specified command line arguments.
This is equivalent to
new CommandLine(command).parseArgs(args); return command;
All this method does is parse the arguments and populate the annotated fields and methods. The caller is responsible for catching any exceptions, handling requests for usage help or version information, and invoking the business logic. Applications may be interested in using the
execute(String...)method instead.- Type Parameters:
T- the type of the annotated object- Parameters:
command- the object to initialize. This object contains fields annotated with@Optionor@Parameters.args- the command line arguments to parse- Returns:
- the specified annotated object
- Throws:
CommandLine.InitializationException- if the specified command object does not have aCommandLine.Command,CommandLine.OptionorCommandLine.ParametersannotationCommandLine.ParameterException- if the specified command line arguments are invalid- Since:
- 0.9.7
- See Also:
execute(String...)
-
populateSpec
public static <T> T populateSpec(Class<T> spec, String... args)
Convenience method that derives the command specification from the specified interface class, and returns an instance of the specified interface. The interface is expected to have annotated getter methods. Picocli will instantiate the interface and the getter methods will return the option and positional parameter values matched on the command line.
This is equivalent to
CommandLine cli = new CommandLine(spec); cli.parse(args); return cli.getCommand();
All this method does is parse the arguments and return an instance whose annotated methods return the specified values. The caller is responsible for catching any exceptions, handling requests for usage help or version information, and invoking the business logic. Applications may be interested in using the
execute(String...)method instead.- Type Parameters:
T- the type of the annotated object- Parameters:
spec- the interface that defines the command specification. This object contains getter methods annotated with@Optionor@Parameters.args- the command line arguments to parse- Returns:
- an instance of the specified annotated interface
- Throws:
CommandLine.InitializationException- if the specified command object does not have aCommandLine.Command,CommandLine.OptionorCommandLine.ParametersannotationCommandLine.ParameterException- if the specified command line arguments are invalid- Since:
- 3.1
- See Also:
execute(String...)
-
parse
@Deprecated public List<CommandLine> parse(String... args)
Deprecated. useparseArgs(String...)insteadExpands any @-files in the specified command line arguments, then parses the arguments and returns a list ofCommandLineobjects representing the top-level command and any subcommands (if any) that were recognized and initialized during the parsing process.If parsing succeeds, the first element in the returned list is always
this CommandLineobject. The returned list may contain more elements if subcommands were registered and these subcommands were initialized by matching command line arguments. If parsing fails, aCommandLine.ParameterExceptionis thrown.All this method does is parse the arguments and populate the annotated fields and methods. The caller is responsible for catching any exceptions, handling requests for usage help or version information, and invoking the business logic. Applications may be interested in using the
execute(String...)method instead.- Parameters:
args- the command line arguments to parse- Returns:
- a list with the top-level command and any subcommands initialized by this method
- Throws:
CommandLine.ParameterException- if the specified command line arguments are invalid; useCommandLine.ParameterException.getCommandLine()to get the command or subcommand whose user input was invalid
-
parseArgs
public CommandLine.ParseResult parseArgs(String... args)
Expands any @-files in the specified command line arguments, then parses the arguments and returns aParseResultwith the options, positional parameters, and subcommands (if any) that were recognized and initialized during the parsing process.If parsing fails, a
CommandLine.ParameterExceptionis thrown.All this method does is parse the arguments and populate the annotated fields and methods. The caller is responsible for catching any exceptions, handling requests for usage help or version information, and invoking the business logic. Applications may be interested in using the
execute(String...)method instead.- Parameters:
args- the command line arguments to parse- Returns:
- a list with the top-level command and any subcommands initialized by this method
- Throws:
CommandLine.ParameterException- if the specified command line arguments are invalid; useCommandLine.ParameterException.getCommandLine()to get the command or subcommand whose user input was invalid- See Also:
execute(String...)
-
getParseResult
public CommandLine.ParseResult getParseResult()
-
getExecutionResult
public <T> T getExecutionResult()
Returns the result of calling the user objectCallableor invoking the user objectMethodafter parsing the user input, ornullif this command has not been executed or if thisCommandLineis for a subcommand that was not specified by the end user on the command line.Implementation note:
It is the responsibility of the
IExecutionStrategyto set this value.- Type Parameters:
T- type of the result value- Returns:
- the result of the user object
CallableorMethod(may benull), ornullif this (sub)command was not executed - Since:
- 4.0
-
setExecutionResult
public void setExecutionResult(Object result)
Sets the result of calling the business logic on the command's user object.- Parameters:
result- the business logic result, may benull- Since:
- 4.0
- See Also:
execute(String...),CommandLine.IExecutionStrategy
-
clearExecutionResults
public void clearExecutionResults()
Clears the execution result of a previous invocation from thisCommandLineand all subcommands.- Since:
- 4.0
-
defaultExceptionHandler
public static CommandLine.DefaultExceptionHandler<List<Object>> defaultExceptionHandler()
Convenience method that returnsnew DefaultExceptionHandler<List<Object>>().
-
printHelpIfRequested
@Deprecated public static boolean printHelpIfRequested(List<CommandLine> parsedCommands, PrintStream out, CommandLine.Help.Ansi ansi)
Deprecated. useprintHelpIfRequested(ParseResult)instead- Since:
- 2.0
-
printHelpIfRequested
public static boolean printHelpIfRequested(CommandLine.ParseResult parseResult)
Delegates toexecuteHelpRequest(ParseResult).- Parameters:
parseResult- contains theCommandLineobjects found during parsing; check these to see if help was requested- Returns:
trueif help was printed,falseotherwise- Since:
- 3.0
-
printHelpIfRequested
@Deprecated public static boolean printHelpIfRequested(List<CommandLine> parsedCommands, PrintStream out, PrintStream err, CommandLine.Help.Ansi ansi)
Deprecated. useexecuteHelpRequest(ParseResult)insteadDelegates to the implementation ofexecuteHelpRequest(ParseResult).- Parameters:
parsedCommands- the list ofCommandLineobjects to check if help was requestedout- thePrintStreamto print help to if requestederr- the error string to print diagnostic messages to, in addition to the output from the exception handleransi- for printing help messages using ANSI styles and colors- Returns:
trueif help was printed,falseotherwise- Since:
- 3.0
-
printHelpIfRequested
@Deprecated public static boolean printHelpIfRequested(List<CommandLine> parsedCommands, PrintStream out, PrintStream err, CommandLine.Help.ColorScheme colorScheme)
Deprecated. useexecuteHelpRequest(ParseResult)insteadDelegates to the implementation ofexecuteHelpRequest(ParseResult).- Parameters:
parsedCommands- the list ofCommandLineobjects to check if help was requestedout- thePrintStreamto print help to if requestederr- the error string to print diagnostic messages to, in addition to the output from the exception handlercolorScheme- for printing help messages using ANSI styles and colors- Returns:
trueif help was printed,falseotherwise- Since:
- 3.6
-
executeHelpRequest
public static Integer executeHelpRequest(CommandLine.ParseResult parseResult)
Helper method that may be useful when processing theParseResultthat results from successfully parsing command line arguments. This method prints out usage help to the configured output writer if requested or version help to the configured output writer if requested and returnsCommandLine.Model.CommandSpec.exitCodeOnUsageHelp()orCommandLine.Model.CommandSpec.exitCodeOnVersionHelp(), respectively. If the command is aCommandLine.Command.helpCommand()andrunnableorcallable, that command is executed and this method returnsCommandLine.Model.CommandSpec.exitCodeOnUsageHelp(). Otherwise, if none of the specifiedCommandLineobjects have help requested, this method returnsnull.Note that this method only looks at the
usageHelpandversionHelpattributes. Thehelpattribute is ignored.Implementation note:
When an error occurs while processing the help request, it is recommended custom Help commands throw a
CommandLine.ParameterExceptionwith a reference to the parent command. This will print the error message and the usage for the parent command, and will use the exit code of the exception handler if one was set.- Parameters:
parseResult- contains theCommandLineobjects found during parsing; check these to see if help was requested- Returns:
CommandLine.Model.CommandSpec.exitCodeOnUsageHelp()if usage help was requested,CommandLine.Model.CommandSpec.exitCodeOnVersionHelp()if version help was requested, andnullotherwise- Since:
- 4.0
- See Also:
CommandLine.IHelpCommandInitializable2
-
execute
public int execute(String... args)
Convenience method to allow command line application authors to avoid some boilerplate code in their application. To use this method, the annotated object that thisCommandLineis constructed with needs to either implementRunnable,Callable, or be aMethodobject. SeegetCommandMethodsfor a convenient way to obtain a commandMethod.This method replaces the
run,callandinvokeconvenience methods that were available with previous versions of picocli.Exit Code
This method returns an exit code that applications can use to call
System.exit. (The return value of theCallableorMethodcan still be obtained viagetExecutionResult.) If the user objectCallableorMethodreturns anintorInteger, this will be used as the exit code. Additionally, if the user object implementsIExitCodeGenerator, an exit code is obtained by calling itsgetExitCode()method (after invoking the user object).In the case of multiple exit codes the highest value will be used (or if all values are negative, the lowest value will be used).
Exception Handling
This method never throws an exception.
If the user specified invalid input, the parameter exception handler is invoked. By default this prints an error message and the usage help message, and returns an exit code.
If an exception occurred while the user object
Runnable,Callable, orMethodwas invoked, this exception is caught and passed to the execution exception handler. The defaultIExecutionExceptionHandlerwill rethrow this Exception.Any exception thrown from the
IParameterExceptionHandlerorIExecutionExceptionHandleris caught, it stacktrace is printed and is mapped to an exit code, using the following logic:If an
IExitCodeExceptionMapperis configured, this mapper is used to determine the exit code based on the exception.If an
IExitCodeExceptionMapperis not set, by default this method will return the@Commandannotation'sexitCodeOnInvalidInputorexitCodeOnExecutionExceptionvalue, respectively.Example Usage:
@Command class MyCommand implements Callable<Integer> { public Integer call() { return 123; } } CommandLine cmd = new CommandLine(new MyCommand()); int exitCode = cmd.execute(args); assert exitCode == 123; System.exit(exitCode);Since
executeis an instance method, not a static method, applications can do configuration before invoking the command. For example:CommandLine cmd = new CommandLine(new MyCallable()) .setCaseInsensitiveEnumValuesAllowed(true) // configure a non-default parser option .setOut(myOutWriter()) // configure an alternative to System.out .setErr(myErrWriter()) // configure an alternative to System.err .setColorScheme(myColorScheme()); // configure a custom color scheme int exitCode = cmd.execute(args); System.exit(exitCode);If the specified command has subcommands, the last subcommand specified on the command line is executed. This can be configured by setting the execution strategy. Built-in alternatives are executing the first subcommand, or executing all specified subcommands.
- Parameters:
args- the command line arguments to parse- Returns:
- the exit code
- Since:
- 4.0
- See Also:
CommandLine.ExitCode,CommandLine.IExitCodeGenerator,getExecutionResult(),getExecutionStrategy(),getParameterExceptionHandler(),getExecutionExceptionHandler(),getExitCodeExceptionMapper()
-
parseWithHandler
@Deprecated public List<Object> parseWithHandler(CommandLine.IParseResultHandler handler, PrintStream out, String... args)
Deprecated. useexecute(String...)andgetExecutionResult()instead- Since:
- 2.0
-
parseWithHandler
@Deprecated public <R> R parseWithHandler(CommandLine.IParseResultHandler2<R> handler, String[] args)
Deprecated. useexecute(String...)andgetExecutionResult()insteadReturns the result of callingparseWithHandlers(IParseResultHandler2, IExceptionHandler2, String...)with a newCommandLine.DefaultExceptionHandlerin addition to the specified parse result handler and the specified command line arguments.This is a convenience method intended to offer the same ease of use as the
runandcallmethods, but with more flexibility and better support for nested subcommands.Calling this method roughly expands to:
try { ParseResult parseResult = parseArgs(args); return handler.handleParseResult(parseResult); } catch (ParameterException ex) { return new DefaultExceptionHandler<R>().handleParseException(ex, args); }Picocli provides some default handlers that allow you to accomplish some common tasks with very little code. The following handlers are available:
CommandLine.RunLasthandler prints help if requested, and otherwise gets the last specified command or subcommand and tries to execute it as aRunnableorCallable.CommandLine.RunFirsthandler prints help if requested, and otherwise executes the top-level command as aRunnableorCallable.CommandLine.RunAllhandler prints help if requested, and otherwise executes all recognized commands and subcommands asRunnableorCallabletasks.CommandLine.DefaultExceptionHandlerprints the error message followed by usage help
- Type Parameters:
R- the return type of this handler- Parameters:
handler- the function that will handle the result of successfully parsing the command line argumentsargs- the command line arguments- Returns:
- an object resulting from handling the parse result or the exception that occurred while parsing the input
- Throws:
CommandLine.ExecutionException- if the command line arguments were parsed successfully but a problem occurred while processing the parse results; useCommandLine.ExecutionException.getCommandLine()to get the command or subcommand where processing failed- Since:
- 3.0
- See Also:
CommandLine.RunLast,CommandLine.RunAll
-
parseWithHandlers
@Deprecated public List<Object> parseWithHandlers(CommandLine.IParseResultHandler handler, PrintStream out, CommandLine.Help.Ansi ansi, CommandLine.IExceptionHandler exceptionHandler, String... args)
Deprecated. useexecute(String...)andgetExecutionResult()instead- Since:
- 2.0
-
parseWithHandlers
@Deprecated public <R> R parseWithHandlers(CommandLine.IParseResultHandler2<R> handler, CommandLine.IExceptionHandler2<R> exceptionHandler, String... args)
Deprecated. useexecute(String...)andgetExecutionResult()insteadTries to parse the specified command line arguments, and if successful, delegates the processing of the resultingParseResultobject to the specified handler. If the command line arguments were invalid, theParameterExceptionthrown from theparsemethod is caught and passed to the specifiedCommandLine.IExceptionHandler2.This is a convenience method intended to offer the same ease of use as the
runandcallmethods, but with more flexibility and better support for nested subcommands.Calling this method roughly expands to:
ParseResult parseResult = null; try { parseResult = parseArgs(args); return handler.handleParseResult(parseResult); } catch (ParameterException ex) { return exceptionHandler.handleParseException(ex, (String[]) args); } catch (ExecutionException ex) { return exceptionHandler.handleExecutionException(ex, parseResult); }Picocli provides some default handlers that allow you to accomplish some common tasks with very little code. The following handlers are available:
CommandLine.RunLasthandler prints help if requested, and otherwise gets the last specified command or subcommand and tries to execute it as aRunnableorCallable.CommandLine.RunFirsthandler prints help if requested, and otherwise executes the top-level command as aRunnableorCallable.CommandLine.RunAllhandler prints help if requested, and otherwise executes all recognized commands and subcommands asRunnableorCallabletasks.CommandLine.DefaultExceptionHandlerprints the error message followed by usage help
- Type Parameters:
R- the return type of the result handler and exception handler- Parameters:
handler- the function that will handle the result of successfully parsing the command line argumentsexceptionHandler- the function that can handle theParameterExceptionthrown when the command line arguments are invalidargs- the command line arguments- Returns:
- an object resulting from handling the parse result or the exception that occurred while parsing the input
- Throws:
CommandLine.ExecutionException- if the command line arguments were parsed successfully but a problem occurred while processing the parse resultParseResultobject; useCommandLine.ExecutionException.getCommandLine()to get the command or subcommand where processing failed- Since:
- 3.0
- See Also:
CommandLine.RunLast,CommandLine.RunAll,CommandLine.DefaultExceptionHandler
-
usage
public static void usage(Object command, PrintStream out)
Equivalent tonew CommandLine(command).usage(out). Seeusage(PrintStream)for details.- Parameters:
command- the object annotated withCommandLine.Command,CommandLine.OptionandCommandLine.Parametersout- the print stream to print the help message to- Throws:
IllegalArgumentException- if the specified command object does not have aCommandLine.Command,CommandLine.OptionorCommandLine.Parametersannotation
-
usage
public static void usage(Object command, PrintStream out, CommandLine.Help.Ansi ansi)
Equivalent tonew CommandLine(command).usage(out, ansi). Seeusage(PrintStream, Help.Ansi)for details.- Parameters:
command- the object annotated withCommandLine.Command,CommandLine.OptionandCommandLine.Parametersout- the print stream to print the help message toansi- whether the usage message should contain ANSI escape codes or not- Throws:
IllegalArgumentException- if the specified command object does not have aCommandLine.Command,CommandLine.OptionorCommandLine.Parametersannotation
-
usage
public static void usage(Object command, PrintStream out, CommandLine.Help.ColorScheme colorScheme)
Equivalent tonew CommandLine(command).usage(out, colorScheme). Seeusage(PrintStream, Help.ColorScheme)for details.- Parameters:
command- the object annotated withCommandLine.Command,CommandLine.OptionandCommandLine.Parametersout- the print stream to print the help message tocolorScheme- theColorSchemedefining the styles for options, parameters and commands when ANSI is enabled- Throws:
IllegalArgumentException- if the specified command object does not have aCommandLine.Command,CommandLine.OptionorCommandLine.Parametersannotation
-
usage
public void usage(PrintStream out)
Delegates tousage(PrintStream, Help.ColorScheme)with the configured color scheme.- Parameters:
out- the printStream to print to- See Also:
usage(PrintStream, Help.ColorScheme)
-
usage
public void usage(PrintWriter writer)
Delegates tousage(PrintWriter, Help.ColorScheme)with the configured color scheme.- Parameters:
writer- the PrintWriter to print to- Since:
- 3.0
- See Also:
usage(PrintWriter, Help.ColorScheme)
-
usage
public void usage(PrintStream out, CommandLine.Help.Ansi ansi)
Delegates tousage(PrintStream, Help.ColorScheme)with the default color scheme.- Parameters:
out- the printStream to print toansi- whether the usage message should include ANSI escape codes or not- See Also:
usage(PrintStream, Help.ColorScheme)
-
usage
public void usage(PrintWriter writer, CommandLine.Help.Ansi ansi)
Similar tousage(PrintStream, Help.Ansi)but with the specifiedPrintWriterinstead of aPrintStream.- Since:
- 3.0
-
usage
public void usage(PrintStream out, CommandLine.Help.ColorScheme colorScheme)
Prints a usage help message for the annotated command class to the specifiedPrintStream. Delegates construction of the usage help message to theCommandLine.Helpinner class and is equivalent to:Help.ColorScheme colorScheme = Help.defaultColorScheme(Help.Ansi.AUTO); Help help = getHelpFactory().create(getCommandSpec(), colorScheme) StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); for (String key : getHelpSectionKeys()) { IHelpSectionRenderer renderer = getHelpSectionMap().get(key); if (renderer != null) { sb.append(renderer.render(help)); } } out.print(sb);Annotate your class with
CommandLine.Commandto control many aspects of the usage help message, including the program name, text of section headings and section contents, and some aspects of the auto-generated sections of the usage help message.To customize the auto-generated sections of the usage help message, like how option details are displayed, instantiate a
CommandLine.Helpobject and use aCommandLine.Help.TextTablewith more of fewer columns, a custom layout, and/or a custom option renderer for ultimate control over which aspects of an Option or Field are displayed where.- Parameters:
out- thePrintStreamto print the usage help message tocolorScheme- theColorSchemedefining the styles for options, parameters and commands when ANSI is enabled- See Also:
CommandLine.Model.UsageMessageSpec
-
usage
public void usage(PrintWriter writer, CommandLine.Help.ColorScheme colorScheme)
Similar tousage(PrintStream, Help.ColorScheme), but with the specifiedPrintWriterinstead of aPrintStream.- Since:
- 3.0
-
getUsageMessage
public String getUsageMessage()
Similar tousage(PrintStream), but returns the usage help message as a String instead of printing it to thePrintStream.- Since:
- 3.2
-
getUsageMessage
public String getUsageMessage(CommandLine.Help.Ansi ansi)
Similar tousage(PrintStream, Help.Ansi), but returns the usage help message as a String instead of printing it to thePrintStream.- Since:
- 3.2
-
getUsageMessage
public String getUsageMessage(CommandLine.Help.ColorScheme colorScheme)
Similar tousage(PrintStream, Help.ColorScheme), but returns the usage help message as a String instead of printing it to thePrintStream.- Since:
- 3.2
-
printVersionHelp
public void printVersionHelp(PrintStream out)
Delegates toprintVersionHelp(PrintStream, Help.Ansi)with the ANSI setting of the configured color scheme.- Parameters:
out- the printStream to print to- Since:
- 0.9.8
- See Also:
printVersionHelp(PrintStream, Help.Ansi)
-
printVersionHelp
public void printVersionHelp(PrintStream out, CommandLine.Help.Ansi ansi)
Prints version information from theCommandLine.Command.version()annotation to the specifiedPrintStream. Each element of the array of version strings is printed on a separate line. Version strings may contain markup for colors and style.- Parameters:
out- the printStream to print toansi- whether the usage message should include ANSI escape codes or not- Since:
- 0.9.8
- See Also:
CommandLine.Command.version(),CommandLine.Option.versionHelp(),isVersionHelpRequested()
-
printVersionHelp
public void printVersionHelp(PrintStream out, CommandLine.Help.Ansi ansi, Object... params)
Prints version information from theCommandLine.Command.version()annotation to the specifiedPrintStream. Each element of the array of version strings is formatted with the specified parameters, and printed on a separate line. Both version strings and parameters may contain markup for colors and style.- Parameters:
out- the printStream to print toansi- whether the usage message should include ANSI escape codes or notparams- Arguments referenced by the format specifiers in the version strings- Since:
- 1.0.0
- See Also:
CommandLine.Command.version(),CommandLine.Option.versionHelp(),isVersionHelpRequested()
-
printVersionHelp
public void printVersionHelp(PrintWriter out)
Delegates toprintVersionHelp(PrintWriter, Help.Ansi, Object...)with the ANSI setting of the configured color scheme.- Parameters:
out- the PrintWriter to print to- Since:
- 4.0
-
printVersionHelp
public void printVersionHelp(PrintWriter out, CommandLine.Help.Ansi ansi, Object... params)
Prints version information from theCommandLine.Command.version()annotation to the specifiedPrintWriter. Each element of the array of version strings is formatted with the specified parameters, and printed on a separate line. Both version strings and parameters may contain markup for colors and style.- Parameters:
out- the PrintWriter to print toansi- whether the usage message should include ANSI escape codes or notparams- Arguments referenced by the format specifiers in the version strings- Since:
- 4.0
- See Also:
CommandLine.Command.version(),CommandLine.Option.versionHelp(),isVersionHelpRequested()
-
call
@Deprecated public static <C extends Callable<T>,T> T call(C callable, String... args)
Deprecated. useexecute(String...)andgetExecutionResult()insteadEquivalent tonew CommandLine(callable).execute(args), except for the return value.- Type Parameters:
C- the annotated object must implement CallableT- the return type of the most specific command (must implementCallable)- Parameters:
callable- the command to call when parsing succeeds.args- the command line arguments to parse- Returns:
nullif an error occurred while parsing the command line options, or if help was requested and printed. Otherwise returns the result of calling the Callable- Throws:
CommandLine.InitializationException- if the specified command object does not have aCommandLine.Command,CommandLine.OptionorCommandLine.ParametersannotationCommandLine.ExecutionException- if the Callable throws an exception- Since:
- 3.0
- See Also:
execute(String...)
-
call
@Deprecated public static <C extends Callable<T>,T> T call(C callable, PrintStream out, String... args)
Deprecated. useexecute(String...)andgetExecutionResult()insteadDelegates tocall(Callable, PrintStream, PrintStream, Help.Ansi, String...)withSystem.errfor diagnostic error messages andCommandLine.Help.Ansi.AUTO.- Type Parameters:
C- the annotated object must implement CallableT- the return type of the most specific command (must implementCallable)- Parameters:
callable- the command to call when parsing succeeds.out- the printStream to print the usage help message to when the user requested helpargs- the command line arguments to parse- Returns:
nullif an error occurred while parsing the command line options, or if help was requested and printed. Otherwise returns the result of calling the Callable- Throws:
CommandLine.InitializationException- if the specified command object does not have aCommandLine.Command,CommandLine.OptionorCommandLine.ParametersannotationCommandLine.ExecutionException- if the Callable throws an exception- See Also:
CommandLine.RunLast
-
call
@Deprecated public static <C extends Callable<T>,T> T call(C callable, PrintStream out, CommandLine.Help.Ansi ansi, String... args)
Deprecated. useexecute(String...)andgetExecutionResult()insteadDelegates tocall(Callable, PrintStream, PrintStream, Help.Ansi, String...)withSystem.errfor diagnostic error messages.- Type Parameters:
C- the annotated object must implement CallableT- the return type of the most specific command (must implementCallable)- Parameters:
callable- the command to call when parsing succeeds.out- the printStream to print the usage help message to when the user requested helpansi- the ANSI style to useargs- the command line arguments to parse- Returns:
nullif an error occurred while parsing the command line options, or if help was requested and printed. Otherwise returns the result of calling the Callable- Throws:
CommandLine.InitializationException- if the specified command object does not have aCommandLine.Command,CommandLine.OptionorCommandLine.ParametersannotationCommandLine.ExecutionException- if the Callable throws an exception- See Also:
CommandLine.RunLast
-
call
@Deprecated public static <C extends Callable<T>,T> T call(C callable, PrintStream out, PrintStream err, CommandLine.Help.Ansi ansi, String... args)
Deprecated. useexecute(String...)andgetExecutionResult()insteadConvenience method to allow command line application authors to avoid some boilerplate code in their application. The annotated object needs to implementCallable.Consider using the
execute(String...)method instead:CommandLine cmd = new CommandLine(callable) .setOut(myOutWriter()) // System.out by default .setErr(myErrWriter()) // System.err by default .setColorScheme(myColorScheme()); // default color scheme, Ansi.AUTO by default int exitCode = cmd.execute(args); //System.exit(exitCode);If the specified Callable command has subcommands, the last subcommand specified on the command line is executed.
- Type Parameters:
C- the annotated object must implement CallableT- the return type of the specifiedCallable- Parameters:
callable- the command to call when parsing succeeds.out- the printStream to print the usage help message to when the user requested helperr- the printStream to print diagnostic messages toansi- including whether the usage message should include ANSI escape codes or notargs- the command line arguments to parse- Returns:
nullif an error occurred while parsing the command line options, or if help was requested and printed. Otherwise returns the result of calling the Callable- Throws:
CommandLine.InitializationException- if the specified command object does not have aCommandLine.Command,CommandLine.OptionorCommandLine.ParametersannotationCommandLine.ExecutionException- if the Callable throws an exception- Since:
- 3.0
-
call
@Deprecated public static <C extends Callable<T>,T> T call(Class<C> callableClass, CommandLine.IFactory factory, String... args)
Deprecated. useexecute(String...)andgetExecutionResult()insteadEquivalent tonew CommandLine(callableClass, factory).execute(args), except for the return value.- Type Parameters:
C- the annotated class must implement CallableT- the return type of the most specific command (must implementCallable)- Parameters:
callableClass- class of the command to call when parsing succeeds.factory- the factory responsible for instantiating the specified callable class and potentially inject other componentsargs- the command line arguments to parse- Returns:
nullif an error occurred while parsing the command line options, or if help was requested and printed. Otherwise returns the result of calling the Callable- Throws:
CommandLine.InitializationException- if the specified class cannot be instantiated by the factory, or does not have aCommandLine.Command,CommandLine.OptionorCommandLine.ParametersannotationCommandLine.ExecutionException- if the Callable throws an exception- Since:
- 3.2
- See Also:
execute(String...)
-
call
@Deprecated public static <C extends Callable<T>,T> T call(Class<C> callableClass, CommandLine.IFactory factory, PrintStream out, String... args)
Deprecated. useexecute(String...)andgetExecutionResult()insteadDelegates tocall(Class, IFactory, PrintStream, PrintStream, Help.Ansi, String...)withSystem.errfor diagnostic error messages, andCommandLine.Help.Ansi.AUTO.- Type Parameters:
C- the annotated class must implement CallableT- the return type of the most specific command (must implementCallable)- Parameters:
callableClass- class of the command to call when parsing succeeds.factory- the factory responsible for instantiating the specified callable class and potentially injecting other componentsout- the printStream to print the usage help message to when the user requested helpargs- the command line arguments to parse- Returns:
nullif an error occurred while parsing the command line options, or if help was requested and printed. Otherwise returns the result of calling the Callable- Throws:
CommandLine.InitializationException- if the specified class cannot be instantiated by the factory, or does not have aCommandLine.Command,CommandLine.OptionorCommandLine.ParametersannotationCommandLine.ExecutionException- if the Callable throws an exception- Since:
- 3.2
-
call
@Deprecated public static <C extends Callable<T>,T> T call(Class<C> callableClass, CommandLine.IFactory factory, PrintStream out, CommandLine.Help.Ansi ansi, String... args)
Deprecated. useexecute(String...)andgetExecutionResult()insteadDelegates tocall(Class, IFactory, PrintStream, PrintStream, Help.Ansi, String...)withSystem.errfor diagnostic error messages.- Type Parameters:
C- the annotated class must implement CallableT- the return type of the most specific command (must implementCallable)- Parameters:
callableClass- class of the command to call when parsing succeeds.factory- the factory responsible for instantiating the specified callable class and potentially injecting other componentsout- the printStream to print the usage help message to when the user requested helpansi- the ANSI style to useargs- the command line arguments to parse- Returns:
nullif an error occurred while parsing the command line options, or if help was requested and printed. Otherwise returns the result of calling the Callable- Throws:
CommandLine.InitializationException- if the specified class cannot be instantiated by the factory, or does not have aCommandLine.Command,CommandLine.OptionorCommandLine.ParametersannotationCommandLine.ExecutionException- if the Callable throws an exception- Since:
- 3.2
-
call
@Deprecated public static <C extends Callable<T>,T> T call(Class<C> callableClass, CommandLine.IFactory factory, PrintStream out, PrintStream err, CommandLine.Help.Ansi ansi, String... args)
Deprecated. useexecute(String...)andgetExecutionResult()insteadConvenience method to allow command line application authors to avoid some boilerplate code in their application. The specified factory will create an instance of the specifiedcallableClass; use this method instead ofcall(Callable, ...)if you want to use a factory that performs Dependency Injection. The annotated class needs to implementCallable.Consider using the
execute(String...)method instead:CommandLine cmd = new CommandLine(callableClass, factory) .setOut(myOutWriter()) // System.out by default .setErr(myErrWriter()) // System.err by default .setColorScheme(myColorScheme()); // default color scheme, Ansi.AUTO by default int exitCode = cmd.execute(args); //System.exit(exitCode);If the specified Callable command has subcommands, the last subcommand specified on the command line is executed.
- Type Parameters:
C- the annotated class must implement CallableT- the return type of the most specific command (must implementCallable)- Parameters:
callableClass- class of the command to call when parsing succeeds.factory- the factory responsible for instantiating the specified callable class and potentially injecting other componentsout- the printStream to print the usage help message to when the user requested helperr- the printStream to print diagnostic messages toansi- the ANSI style to useargs- the command line arguments to parse- Returns:
nullif an error occurred while parsing the command line options, or if help was requested and printed. Otherwise returns the result of calling the Callable- Throws:
CommandLine.InitializationException- if the specified class cannot be instantiated by the factory, or does not have aCommandLine.Command,CommandLine.OptionorCommandLine.ParametersannotationCommandLine.ExecutionException- if the Callable throws an exception- Since:
- 3.2
-
run
@Deprecated public static <R extends Runnable> void run(R runnable, String... args)
Deprecated. useexecute(String...)insteadEquivalent tonew CommandLine(runnable).execute(args).- Type Parameters:
R- the annotated object must implement Runnable- Parameters:
runnable- the command to run when parsing succeeds.args- the command line arguments to parse- Throws:
CommandLine.InitializationException- if the specified command object does not have aCommandLine.Command,CommandLine.OptionorCommandLine.ParametersannotationCommandLine.ExecutionException- if the Runnable throws an exception- Since:
- 3.0
- See Also:
execute(String...)
-
run
@Deprecated public static <R extends Runnable> void run(R runnable, PrintStream out, String... args)
Deprecated. useexecute(String...)insteadDelegates torun(Runnable, PrintStream, PrintStream, Help.Ansi, String...)withSystem.errfor diagnostic error messages andCommandLine.Help.Ansi.AUTO.- Type Parameters:
R- the annotated object must implement Runnable- Parameters:
runnable- the command to run when parsing succeeds.out- the printStream to print the usage help message to when the user requested helpargs- the command line arguments to parse- Throws:
CommandLine.InitializationException- if the specified command object does not have aCommandLine.Command,CommandLine.OptionorCommandLine.ParametersannotationCommandLine.ExecutionException- if the Runnable throws an exception- See Also:
CommandLine.RunLast
-
run
@Deprecated public static <R extends Runnable> void run(R runnable, PrintStream out, CommandLine.Help.Ansi ansi, String... args)
Deprecated. useexecute(String...)insteadDelegates torun(Runnable, PrintStream, PrintStream, Help.Ansi, String...)withSystem.errfor diagnostic error messages.- Type Parameters:
R- the annotated object must implement Runnable- Parameters:
runnable- the command to run when parsing succeeds.out- the printStream to print the usage help message to when the user requested helpansi- whether the usage message should include ANSI escape codes or notargs- the command line arguments to parse- Throws:
CommandLine.InitializationException- if the specified command object does not have aCommandLine.Command,CommandLine.OptionorCommandLine.ParametersannotationCommandLine.ExecutionException- if the Runnable throws an exception- See Also:
CommandLine.RunLast
-
run
@Deprecated public static <R extends Runnable> void run(R runnable, PrintStream out, PrintStream err, CommandLine.Help.Ansi ansi, String... args)
Deprecated. useexecute(String...)insteadConvenience method to allow command line application authors to avoid some boilerplate code in their application. The annotated object needs to implementRunnable.Consider using the
execute(String...)method instead:CommandLine cmd = new CommandLine(runnable) .setOut(myOutWriter()) // System.out by default .setErr(myErrWriter()) // System.err by default .setColorScheme(myColorScheme()); // default color scheme, Ansi.AUTO by default int exitCode = cmd.execute(args); //System.exit(exitCode);If the specified Runnable command has subcommands, the last subcommand specified on the command line is executed.
From picocli v2.0, this method prints usage help or version help if requested, and any exceptions thrown by the
Runnableare caught and rethrown wrapped in anExecutionException.- Type Parameters:
R- the annotated object must implement Runnable- Parameters:
runnable- the command to run when parsing succeeds.out- the printStream to print the usage help message to when the user requested helperr- the printStream to print diagnostic messages toansi- whether the usage message should include ANSI escape codes or notargs- the command line arguments to parse- Throws:
CommandLine.InitializationException- if the specified command object does not have aCommandLine.Command,CommandLine.OptionorCommandLine.ParametersannotationCommandLine.ExecutionException- if the Runnable throws an exception- Since:
- 3.0
-
run
@Deprecated public static <R extends Runnable> void run(Class<R> runnableClass, CommandLine.IFactory factory, String... args)
Deprecated. useexecute(String...)insteadEquivalent tonew CommandLine(runnableClass, factory).execute(args).- Type Parameters:
R- the annotated class must implement Runnable- Parameters:
runnableClass- class of the command to run when parsing succeeds.factory- the factory responsible for instantiating the specified Runnable class and potentially injecting other componentsargs- the command line arguments to parse- Throws:
CommandLine.InitializationException- if the specified class cannot be instantiated by the factory, or does not have aCommandLine.Command,CommandLine.OptionorCommandLine.ParametersannotationCommandLine.ExecutionException- if the Runnable throws an exception- Since:
- 3.2
- See Also:
execute(String...)
-
run
@Deprecated public static <R extends Runnable> void run(Class<R> runnableClass, CommandLine.IFactory factory, PrintStream out, String... args)
Deprecated. useexecute(String...)insteadDelegates torun(Class, IFactory, PrintStream, PrintStream, Help.Ansi, String...)withSystem.errfor diagnostic error messages, andCommandLine.Help.Ansi.AUTO.- Type Parameters:
R- the annotated class must implement Runnable- Parameters:
runnableClass- class of the command to run when parsing succeeds.factory- the factory responsible for instantiating the specified Runnable class and potentially injecting other componentsout- the printStream to print the usage help message to when the user requested helpargs- the command line arguments to parse- Throws:
CommandLine.InitializationException- if the specified class cannot be instantiated by the factory, or does not have aCommandLine.Command,CommandLine.OptionorCommandLine.ParametersannotationCommandLine.ExecutionException- if the Runnable throws an exception- Since:
- 3.2
- See Also:
run(Class, IFactory, PrintStream, PrintStream, Help.Ansi, String...),parseWithHandlers(IParseResultHandler2, IExceptionHandler2, String...),CommandLine.RunLast
-
run
@Deprecated public static <R extends Runnable> void run(Class<R> runnableClass, CommandLine.IFactory factory, PrintStream out, CommandLine.Help.Ansi ansi, String... args)
Deprecated. useexecute(String...)insteadDelegates torun(Class, IFactory, PrintStream, PrintStream, Help.Ansi, String...)withSystem.errfor diagnostic error messages.- Type Parameters:
R- the annotated class must implement Runnable- Parameters:
runnableClass- class of the command to run when parsing succeeds.factory- the factory responsible for instantiating the specified Runnable class and potentially injecting other componentsout- the printStream to print the usage help message to when the user requested helpansi- whether the usage message should include ANSI escape codes or notargs- the command line arguments to parse- Throws:
CommandLine.InitializationException- if the specified class cannot be instantiated by the factory, or does not have aCommandLine.Command,CommandLine.OptionorCommandLine.ParametersannotationCommandLine.ExecutionException- if the Runnable throws an exception- Since:
- 3.2
- See Also:
run(Class, IFactory, PrintStream, PrintStream, Help.Ansi, String...),parseWithHandlers(IParseResultHandler2, IExceptionHandler2, String...),CommandLine.RunLast
-
run
@Deprecated public static <R extends Runnable> void run(Class<R> runnableClass, CommandLine.IFactory factory, PrintStream out, PrintStream err, CommandLine.Help.Ansi ansi, String... args)
Deprecated. useexecute(String...)insteadConvenience method to allow command line application authors to avoid some boilerplate code in their application. The specified factory will create an instance of the specifiedrunnableClass; use this method instead ofrun(Runnable, ...)if you want to use a factory that performs Dependency Injection. The annotated class needs to implementRunnable.Consider using the
execute(String...)method instead:CommandLine cmd = new CommandLine(runnableClass, factory) .setOut(myOutWriter()) // System.out by default .setErr(myErrWriter()) // System.err by default .setColorScheme(myColorScheme()); // default color scheme, Ansi.AUTO by default int exitCode = cmd.execute(args); //System.exit(exitCode);If the specified Runnable command has subcommands, the last subcommand specified on the command line is executed.
This method prints usage help or version help if requested, and any exceptions thrown by the
Runnableare caught and rethrown wrapped in anExecutionException.- Type Parameters:
R- the annotated class must implement Runnable- Parameters:
runnableClass- class of the command to run when parsing succeeds.factory- the factory responsible for instantiating the specified Runnable class and potentially injecting other componentsout- the printStream to print the usage help message to when the user requested helperr- the printStream to print diagnostic messages toansi- whether the usage message should include ANSI escape codes or notargs- the command line arguments to parse- Since:
- 3.2
-
invoke
@Deprecated public static Object invoke(String methodName, Class<?> cls, String... args)
Deprecated. useexecute(String...)andgetExecutionResult()insteadDelegates toinvoke(String, Class, PrintStream, PrintStream, Help.Ansi, String...)withSystem.outfor requested usage help messages,System.errfor diagnostic error messages, andCommandLine.Help.Ansi.AUTO.- Parameters:
methodName- the@Command-annotated method to build aCommandLine.Model.CommandSpecmodel from, and run when parsing succeeds.cls- the class where the@Command-annotated method is declared, or a subclassargs- the command line arguments to parse- Throws:
CommandLine.InitializationException- if the specified method does not have aCommandLine.Commandannotation, or if the specified class contains multiple@Command-annotated methods with the specified nameCommandLine.ExecutionException- if the Runnable throws an exception- Since:
- 3.6
- See Also:
invoke(String, Class, PrintStream, PrintStream, Help.Ansi, String...),parseWithHandlers(IParseResultHandler2, IExceptionHandler2, String...)
-
invoke
@Deprecated public static Object invoke(String methodName, Class<?> cls, PrintStream out, String... args)
Deprecated. useexecute(String...)andgetExecutionResult()insteadDelegates toinvoke(String, Class, PrintStream, PrintStream, Help.Ansi, String...)with the specified stream for requested usage help messages,System.errfor diagnostic error messages, andCommandLine.Help.Ansi.AUTO.- Parameters:
methodName- the@Command-annotated method to build aCommandLine.Model.CommandSpecmodel from, and run when parsing succeeds.cls- the class where the@Command-annotated method is declared, or a subclassout- the printstream to print requested help message toargs- the command line arguments to parse- Throws:
CommandLine.InitializationException- if the specified method does not have aCommandLine.Commandannotation, or if the specified class contains multiple@Command-annotated methods with the specified nameCommandLine.ExecutionException- if the Runnable throws an exception- Since:
- 3.6
- See Also:
invoke(String, Class, PrintStream, PrintStream, Help.Ansi, String...),parseWithHandlers(IParseResultHandler2, IExceptionHandler2, String...)
-
invoke
@Deprecated public static Object invoke(String methodName, Class<?> cls, PrintStream out, CommandLine.Help.Ansi ansi, String... args)
Deprecated. useexecute(String...)andgetExecutionResult()insteadDelegates toinvoke(String, Class, PrintStream, PrintStream, Help.Ansi, String...)with the specified stream for requested usage help messages,System.errfor diagnostic error messages, and the specified Ansi mode.- Parameters:
methodName- the@Command-annotated method to build aCommandLine.Model.CommandSpecmodel from, and run when parsing succeeds.cls- the class where the@Command-annotated method is declared, or a subclassout- the printstream to print requested help message toansi- whether the usage message should include ANSI escape codes or notargs- the command line arguments to parse- Throws:
CommandLine.InitializationException- if the specified method does not have aCommandLine.Commandannotation, or if the specified class contains multiple@Command-annotated methods with the specified nameCommandLine.ExecutionException- if the Runnable throws an exception- Since:
- 3.6
- See Also:
invoke(String, Class, PrintStream, PrintStream, Help.Ansi, String...),parseWithHandlers(IParseResultHandler2, IExceptionHandler2, String...)
-
invoke
@Deprecated public static Object invoke(String methodName, Class<?> cls, PrintStream out, PrintStream err, CommandLine.Help.Ansi ansi, String... args)
Deprecated. useexecute(String...)andgetExecutionResult()insteadConvenience method to allow command line application authors to avoid some boilerplate code in their application. Constructs aCommandLine.Model.CommandSpecmodel from the@Optionand@Parameters-annotated method parameters of the@Command-annotated method, parses the specified command line arguments and invokes the specified method.Consider using the
execute(String...)method instead:Method commandMethod = getCommandMethods(cls, methodName).get(0); CommandLine cmd = new CommandLine(commandMethod) .setOut(myOutWriter()) // System.out by default .setErr(myErrWriter()) // System.err by default .setColorScheme(myColorScheme()); // default color scheme, Ansi.AUTO by default int exitCode = cmd.execute(args); //System.exit(exitCode);- Parameters:
methodName- the@Command-annotated method to build aCommandLine.Model.CommandSpecmodel from, and run when parsing succeeds.cls- the class where the@Command-annotated method is declared, or a subclassout- the printStream to print the usage help message to when the user requested helperr- the printStream to print diagnostic messages toansi- whether the usage message should include ANSI escape codes or notargs- the command line arguments to parse- Throws:
CommandLine.InitializationException- if the specified method does not have aCommandLine.Commandannotation, or if the specified class contains multiple@Command-annotated methods with the specified nameCommandLine.ExecutionException- if the method throws an exception- Since:
- 3.6
-
getCommandMethods
public static List<Method> getCommandMethods(Class<?> cls, String methodName)
Helper to get methods of a class annotated with@Commandvia reflection, optionally filtered by method name (not@Command.name). Methods have to be either public (inherited) members or be declared bycls, that is "inherited" static or protected methods will not be picked up.- Parameters:
cls- the class to search for methods annotated with@CommandmethodName- if notnull, return only methods whose method name (not@Command.name) equals this string. Ignored ifnull.- Returns:
- the matching command methods, or an empty list
- Since:
- 3.6.0
- See Also:
invoke(String, Class, String...)
-
registerConverter
public <K> CommandLine registerConverter(Class<K> cls, CommandLine.ITypeConverter<K> converter)
Registers the specified type converter for the specified class. When initializing fields annotated withCommandLine.Option, the field's type is used as a lookup key to find the associated type converter, and this type converter converts the original command line argument string value to the correct type.Java 8 lambdas make it easy to register custom type converters:
commandLine.registerConverter(java.nio.file.Path.class, s -> java.nio.file.Paths.get(s)); commandLine.registerConverter(java.time.Duration.class, s -> java.time.Duration.parse(s));
Built-in type converters are pre-registered for the following java 1.5 types:
- all primitive types
- all primitive wrapper types: Boolean, Byte, Character, Double, Float, Integer, Long, Short
- any enum
- java.io.File
- java.math.BigDecimal
- java.math.BigInteger
- java.net.InetAddress
- java.net.URI
- java.net.URL
- java.nio.charset.Charset
- java.sql.Time
- java.util.Date
- java.util.UUID
- java.util.regex.Pattern
- StringBuilder
- CharSequence
- String
The specified converter will be registered with this
CommandLineand the full hierarchy of its subcommands and nested sub-subcommands at the moment the converter is registered. Subcommands added later will not have this converter added automatically. To ensure a custom type converter is available to all subcommands, register the type converter last, after adding subcommands.- Type Parameters:
K- the target type- Parameters:
cls- the target class to convert parameter string values toconverter- the class capable of converting string values to the specified target type- Returns:
- this CommandLine object, to allow method chaining
- See Also:
addSubcommand(String, Object)
-
getSeparator
public String getSeparator()
Returns the String that separates option names from option values when parsing command line options.- Returns:
- the String the parser uses to separate option names from option values
- See Also:
CommandLine.Model.ParserSpec.separator()
-
setSeparator
public CommandLine setSeparator(String separator)
Sets the String the parser uses to separate option names from option values to the specified value. The separator may also be set declaratively with theCommandLine.Command.separator()annotation attribute.The specified setting will be registered with this
CommandLineand the full hierarchy of its subcommands and nested sub-subcommands at the moment this method is called. Subcommands added later will have the default setting. To ensure a setting is applied to all subcommands, call the setter last, after adding subcommands.- Parameters:
separator- the String that separates option names from option values- Returns:
- this
CommandLineobject, to allow method chaining - See Also:
CommandLine.Model.ParserSpec.separator(String)
-
getResourceBundle
public ResourceBundle getResourceBundle()
Returns the ResourceBundle of this command ornullif no resource bundle is set.- Since:
- 3.6
- See Also:
CommandLine.Command.resourceBundle(),CommandLine.Model.CommandSpec.resourceBundle()
-
setResourceBundle
public CommandLine setResourceBundle(ResourceBundle bundle)
Sets the ResourceBundle containing usage help message strings.The specified bundle will be registered with this
CommandLineand the full hierarchy of its subcommands and nested sub-subcommands at the moment this method is called. Subcommands added later will not be impacted. To ensure a setting is applied to all subcommands, call the setter last, after adding subcommands.- Parameters:
bundle- the ResourceBundle containing usage help message strings- Returns:
- this
CommandLineobject, to allow method chaining - Since:
- 3.6
- See Also:
CommandLine.Command.resourceBundle(),CommandLine.Model.CommandSpec.resourceBundle(ResourceBundle)
-
getUsageHelpWidth
public int getUsageHelpWidth()
Returns the maximum width of the usage help message. The default is 80.
-
setUsageHelpWidth
public CommandLine setUsageHelpWidth(int width)
Sets the maximum width of the usage help message. Longer lines are wrapped.The specified setting will be registered with this
CommandLineand the full hierarchy of its subcommands and nested sub-subcommands at the moment this method is called. Subcommands added later will have the default setting. To ensure a setting is applied to all subcommands, call the setter last, after adding subcommands.- Parameters:
width- the maximum width of the usage help message- Returns:
- this
CommandLineobject, to allow method chaining - See Also:
CommandLine.Model.UsageMessageSpec.width(int)
-
getUsageHelpLongOptionsMaxWidth
public int getUsageHelpLongOptionsMaxWidth()
Returns the maximum usage help long options column max width to the specified value. This value controls the maximum width of the long options column: any positional parameter labels or long options that are longer than the specified value will overflow into the description column, and cause the description to be displayed on the next line.- Since:
- 4.2
- See Also:
CommandLine.Model.UsageMessageSpec.longOptionsMaxWidth()
-
setUsageHelpLongOptionsMaxWidth
public CommandLine setUsageHelpLongOptionsMaxWidth(int columnWidth)
Returns the maximum usage help long options column max width to the specified value. This value controls the maximum width of the long options column: any positional parameter labels or long options that are longer than the specified value will overflow into the description column, and cause the description to be displayed on the next line.The specified setting will be registered with this
CommandLineand the full hierarchy of its subcommands and nested sub-subcommands at the moment this method is called. Subcommands added later will have the default setting. To ensure a setting is applied to all subcommands, call the setter last, after adding subcommands.- Parameters:
columnWidth- the new maximum usage help long options column max width. Must be 20 or greater.- Returns:
- this
CommandLineobject, to allow method chaining - Since:
- 4.2
- See Also:
CommandLine.Model.UsageMessageSpec.longOptionsMaxWidth(int)
-
isUsageHelpAutoWidth
public boolean isUsageHelpAutoWidth()
Returns whether picocli should attempt to detect the terminal size and adjust the usage help message width to take the full terminal width. End users may enable this by setting system property"picocli.usage.width"toAUTO, and may disable this by setting this system property to a numeric value. This feature requires Java 7 or greater. The default isfalse.- Since:
- 4.0
- See Also:
CommandLine.Model.UsageMessageSpec.autoWidth()
-
setUsageHelpAutoWidth
public CommandLine setUsageHelpAutoWidth(boolean detectTerminalSize)
Sets whether picocli should attempt to detect the terminal size and adjust the usage help message width to take the full terminal width. The default isfalse.The specified setting will be registered with this
CommandLineand the full hierarchy of its subcommands and nested sub-subcommands at the moment this method is called. Subcommands added later will have the default setting. To ensure a setting is applied to all subcommands, call the setter last, after adding subcommands.- Parameters:
detectTerminalSize- whether picocli should attempt to detect the terminal size- Returns:
- this
CommandLineobject, to allow method chaining - Since:
- 4.0
- See Also:
CommandLine.Model.UsageMessageSpec.autoWidth(boolean)
-
getCommandName
public String getCommandName()
Returns the command name (also called program name) displayed in the usage help synopsis.- Returns:
- the command name (also called program name) displayed in the usage
- Since:
- 2.0
- See Also:
CommandLine.Model.CommandSpec.name()
-
setCommandName
public CommandLine setCommandName(String commandName)
Sets the command name (also called program name) displayed in the usage help synopsis to the specified value. Note that this method only modifies the usage help message, it does not impact parsing behaviour. The command name may also be set declaratively with theCommandLine.Command.name()annotation attribute.- Parameters:
commandName- command name (also called program name) displayed in the usage help synopsis- Returns:
- this
CommandLineobject, to allow method chaining - Since:
- 2.0
- See Also:
CommandLine.Model.CommandSpec.name(String)
-
isExpandAtFiles
public boolean isExpandAtFiles()
Returns whether arguments starting with'@'should be treated as the path to an argument file and its contents should be expanded into separate arguments for each line in the specified file. This property istrueby default.- Returns:
- whether "argument files" or
@filesshould be expanded into their content - Since:
- 2.1
- See Also:
CommandLine.Model.ParserSpec.expandAtFiles()
-
setExpandAtFiles
public CommandLine setExpandAtFiles(boolean expandAtFiles)
Sets whether arguments starting with'@'should be treated as the path to an argument file and its contents should be expanded into separate arguments for each line in the specified file. (trueby default.)- Parameters:
expandAtFiles- whether "argument files" or@filesshould be expanded into their content- Returns:
- this
CommandLineobject, to allow method chaining - Since:
- 2.1
- See Also:
CommandLine.Model.ParserSpec.expandAtFiles(boolean)
-
getAtFileCommentChar
public Character getAtFileCommentChar()
Returns the character that starts a single-line comment ornullif all content of argument files should be interpreted as arguments (without comments). If specified, all characters from the comment character to the end of the line are ignored.- Returns:
- the character that starts a single-line comment or
null. The default is'#'. - Since:
- 3.5
- See Also:
CommandLine.Model.ParserSpec.atFileCommentChar()
-
setAtFileCommentChar
public CommandLine setAtFileCommentChar(Character atFileCommentChar)
Sets the character that starts a single-line comment ornullif all content of argument files should be interpreted as arguments (without comments). If specified, all characters from the comment character to the end of the line are ignored.- Parameters:
atFileCommentChar- the character that starts a single-line comment ornull. The default is'#'.- Returns:
- this
CommandLineobject, to allow method chaining - Since:
- 3.5
- See Also:
CommandLine.Model.ParserSpec.atFileCommentChar(Character)
-
isUseSimplifiedAtFiles
public boolean isUseSimplifiedAtFiles()
Returns whether to use a simplified argument file format that is compatible with JCommander. In this format, every line (except empty lines and comment lines) is interpreted as a single argument. Arguments containing whitespace do not need to be quoted. When system property"picocli.useSimplifiedAtFiles"is defined, the system property value overrides the programmatically set value.- Returns:
- whether to use a simplified argument file format. The default is
false. - Since:
- 3.9
- See Also:
CommandLine.Model.ParserSpec.useSimplifiedAtFiles()
-
setUseSimplifiedAtFiles
public CommandLine setUseSimplifiedAtFiles(boolean simplifiedAtFiles)
Sets whether to use a simplified argument file format that is compatible with JCommander. In this format, every line (except empty lines and comment lines) is interpreted as a single argument. Arguments containing whitespace do not need to be quoted. When system property"picocli.useSimplifiedAtFiles"is defined, the system property value overrides the programmatically set value.- Parameters:
simplifiedAtFiles- whether to use a simplified argument file format. The default isfalse.- Returns:
- this
CommandLineobject, to allow method chaining - Since:
- 3.9
- See Also:
CommandLine.Model.ParserSpec.useSimplifiedAtFiles(boolean)
-
getNegatableOptionTransformer
public CommandLine.INegatableOptionTransformer getNegatableOptionTransformer()
Returns theINegatableOptionTransformerused to create the negative form of negatable options. By default this returns the result ofCommandLine.RegexTransformer.createDefault().- Returns:
- the
INegatableOptionTransformerused to create negative option names. - Since:
- 4.0
- See Also:
CommandLine.Option.negatable(),CommandLine.Model.CommandSpec.negatableOptionTransformer()
-
setNegatableOptionTransformer
public CommandLine setNegatableOptionTransformer(CommandLine.INegatableOptionTransformer transformer)
Sets theINegatableOptionTransformerused to create the negative form of negatable options.The specified setting will be registered with this
Note thatCommandLineand the full hierarchy of its subcommands and nested sub-subcommands at the moment this method is called. Subcommands added later will have the default setting. To ensure a setting is applied to all subcommands, call the setter last, after adding subcommands.setOptionsCaseInsensitive(boolean)will also change the case sensitivity of negatable options: any customCommandLine.INegatableOptionTransformerthat was previously installed will be replaced by the case-insensitive version of the default transformer. To ensure your custom transformer is used, install it last, after changing case sensitivity.- Parameters:
transformer- theINegatableOptionTransformerused to create negative option names.- Returns:
- this
CommandLineobject, to allow method chaining - Since:
- 4.0
- See Also:
CommandLine.Option.negatable(),CommandLine.Model.CommandSpec.negatableOptionTransformer(CommandLine.INegatableOptionTransformer)
-
defaultFactory
public static CommandLine.IFactory defaultFactory()
Returns the defaultCommandLine.IFactoryimplementation used if no factory was specified in theCommandLine constructor.This implementation has special logic for instantiating
CollectionsandMaps, and otherwise tries to create an instance by invoking the default constructor of the specified class.Special logic for instantiating Collections and Maps:
// if class is an interface that extends java.util.Collection, return a new instance of: 1. List -> ArrayList 2. SortedSet -> TreeSet 3. Set -> LinkedHashSet 4. Queue -> LinkedList 5. Collection -> ArrayList // if extending or implementing java.util.Map: 1. try invoking the default constructor; return this on success. 2. if this fails, return a LinkedHashMap- Since:
- 4.0
-
tracer
public static CommandLine.Tracer tracer()
Returns theTracerused internally for printing internal debug statements.- Returns:
- the
Tracerused internally for printing internal debug statements - Since:
- 4.7.7
-
-