简介
Picocli是一个单文件命令行解析框架,它允许您创建命令行应用而几乎不需要代码。使用 @Option 或 @Parameters
在您的应用中注释字段,Picocli将分别使用命令行选项和位置参数填充这些字段。例如:
@Command(name = "Greet", header = "%n@|green Hello world demo|@")
class Greet implements Runnable {
@Option(names = {"-u", "--user"}, required = true, description = "The user name.")
String userName;
public void run() {
System.out.println("Hello, " + userName);
}
public static void main(String... args) {
CommandLine.run(new Greet(), System.err, args);
}
}当我们执行这个程序时,Picocli会解析命令行,并在调用 run 方法之前填充 userName 字段:
$ java Greet -u picocli
Hello, picocliPicocli采用 Ansi颜色和样式生成使用帮助消息。如果我们进行无效输入来运行上面的程序(缺少必须的用户名选项), picocli会输出一条错误和使用帮助信息:
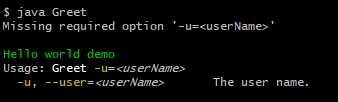
用户手册详细描述了picocli的功能。本文重点介绍Picocli 2.0版本中引入的新功能。
带位置参数的混合选项
我们对解析器进行了改进,现在位置参数现在可以与命令行上的选项混在一起。

以前,位置参数必须紧随选项。 从此版本开始,任何非选项或子命令的命令行参数都将被解释为位置参数。
例如:
class MixDemo implements Runnable {
@Option(names = "-o")
List<String> options;
@Parameters
List<String> positional;
public void run() {
System.out.println("positional: " + positional);
System.out.println("options : " + options);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
CommandLine.run(new MixDemo(), System.err, args);
}
}使用选项和位置参数的混合来运行上面的类表明,非选项被认为是位置参数。例如:
$ java MixDemo param0 -o AAA param1 param2 -o BBB param3
positional: [param0, param1, param2, param3]
options : [AAA, BBB]为了支持具有位置参数的混合选项,已对解析器进行更改。 从 picocl2.0开始,多值选项(数组、列表和映射字段)不再默认为贪婪的。 2.0版本详细描述了此变化和其他 潜在的重大变更。
发现集合类型
Picocli将命令行参数的 自动类型转换执行到带注释字段的类型。命名选项和位置参数都可以是强类型。

在v2.0之前,picocli需要使用 type 属性对 Collection 和 Map 字段进行注释,
以便能够进行类型转换。对于具有其他类型的字段,像数组字段和单值字段,如 int 或 java.io.File 字段,picocli自动从字段类型中检测目标类型,但是集合和映射需要更详细的注释。例如:
class Before {
@Option(names = "-u", type = {TimeUnit.class, Long.class})
Map<TimeUnit, Long> timeout;
@Parameters(type = File.class)
List<File> files;
}从v2.0开始,type 属性不再是 Collection 和 Map 字段的必要属性:picocli将从泛型类型推断集合元素类型。
type 属性仍然像以前一样工作,只是在大多数情况下是可选的。
省略 type 属性会删除一些重复的内容,从而使代码更简洁、更清晰:
class Current {
@Option(names = "-u")
Map<TimeUnit, Long> timeout;
@Parameters
List<File> files;
}在上面的示例中,picocli 2.0能够自动发现,命令行参数在添加到列表之前需要转换为 File,以及对于映射,需要将键转换为 TimeUnit,将值转换为 Long 。
自动帮助
Picocli提供了许多便利方法,如 run 和 call,它们能够解析命令行参数、处理错误并调用接口方法来执行应用。
从此版本开始,当用户在命令行中指定一个注释有 versionHelp 或 usageHelp 属性的选项时,这些便利方法还将自动输出使用帮助和版本信息。

下面的示例程序演示自动帮助:
@Command(version = "Help demo v1.2.3", header = "%nAutomatic Help Demo%n",
description = "Prints usage help and version help when requested.%n")
class AutomaticHelpDemo implements Runnable {
@Option(names = "--count", description = "The number of times to repeat.")
int count;
@Option(names = {"-h", "--help"}, usageHelp = true,
description = "Print usage help and exit.")
boolean usageHelpRequested;
@Option(names = {"-V", "--version"}, versionHelp = true,
description = "Print version information and exit.")
boolean versionHelpRequested;
public void run() {
// NOTE: code like below is no longer required:
//
// if (usageHelpRequested) {
// new CommandLine(this).usage(System.err);
// } else if (versionHelpRequested) {
// new CommandLine(this).printVersionHelp(System.err);
// } else { ... the business logic
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
System.out.println("Hello world");
}
}
public static void main(String... args) {
CommandLine.run(new AutomaticHelpDemo(), System.err, args);
}
}当使用 -h 或 --help 执行时,程序输出使用帮助:
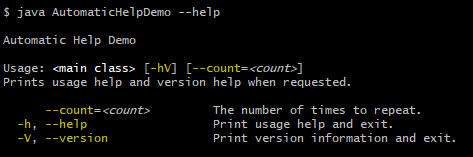
类似地,当使用 -V 或 --version 执行时,程序输出版本信息:
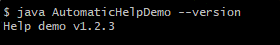
自动输出帮助的方法:
-
CommandLine::call
-
CommandLine::run
-
CommandLine::parseWithHandler (通过内置Run…句柄)
-
CommandLine::parseWithHandlers (通过内置Run…句柄)
不自动输出帮助的方法:
-
CommandLine::parse
-
CommandLine::populateCommand
更好的子命令支持
此版本添加了新的 CommandLine::parseWithHandler 方法。这些方法提供了与 run 和 call 方法相同的易用性,但是对于嵌套的子命令有了更大的灵活性和更好的支持。

考虑具有子命令的应用需要做什么:
-
解析命令行。
-
如果用户输入无效,则对解析失败处的子命令输出错误消息和使用帮助消息。
-
如果解析成功,则检查用户是否已请求顶层命令或子命令的使用帮助或版本信息。如果是,则输出请求的信息并退出。
-
否则,执行业务逻辑。通常这意味着执行最具体的子命令。
Picocli提供了一些构造块来完成此任务,但是将它们连接在一起取决于应用。这种连接本质上是样板,且它在应用之间非常相似。例如,以前,具有子命令的应用通常包含如下代码:
public static void main(String... args) {
// 1. parse the command line
CommandLine top = new CommandLine(new YourApp());
List<CommandLine> parsedCommands;
try {
parsedCommands = top.parse(args);
} catch (ParameterException ex) {
// 2. handle incorrect user input for one of the subcommands
System.err.println(ex.getMessage());
ex.getCommandLine().usage(System.err);
return;
}
// 3. check if the user requested help
for (CommandLine parsed : parsedCommands) {
if (parsed.isUsageHelpRequested()) {
parsed.usage(System.err);
return;
} else if (parsed.isVersionHelpRequested()) {
parsed.printVersionHelp(System.err);
return;
}
}
// 4. execute the most specific subcommand
Object last = parsedCommands.get(parsedCommands.size() - 1).getCommand();
if (last instanceof Runnable) {
((Runnable) last).run();
} else if (last instanceof Callable) {
Object result = ((Callable) last).call();
// ... do something with result
} else {
throw new ExecutionException("Not a Runnable or Callable");
}
}这是相当大的样板代码量。Picocli 2.0提供了一种便利方法,它允许您将上述所有内容缩减为一行代码,这样您就可以专注于您应用的业务逻辑:
public static void main(String... args) {
// This handles all of the above in one line:
// 1. parse the command line
// 2. handle incorrect user input for one of the subcommands
// 3. automatically print help if requested
// 4. execute one or more subcommands
new CommandLine(new YourApp()).parseWithHandler(new RunLast(), System.err, args);
}新的便利方法是 parseWithHandler 。您可以创建自己的自定义句柄或使用其中一个内置句柄。Picocli提供一些常见用例的句柄实现。
内置的句柄是 RunFirst、RunLast 和 RunAll。所有这些句柄都提供了自动帮助:如果用户请求usageHelp或versionHelp,
将输出所请求的信息,句柄将返回,而无需进一步处理。句柄希望所有命令都能执行 java.lang.Runnable 或 java.util.concurrent.Callable。
-
RunLast执行*最具体的*命令或子命令。例如,如果用户调用java Git commit -m "commit message", 那么picocli认为Git是顶层命令,commit为子命令。在这个例子中,commit子命令是最具体的命令,所以RunLast将只执行子命令。 如果没有子命令,将执行顶层命令。现在RunLast由Picocli内部用于执行现有的CommandLine::run和CommandLine::call的便利方法。 -
RunFirst只执行*首个*、顶层命令,并忽略子命令。 -
RunAll执行命令行中出现的*顶层命令和所有子命令。
还有一个 parseWithHandlers 方法,它与前面的方法类似,但额外允许您为不正确的用户输入指定一个自定义的句柄。
改进的 'run' 和 'call' 方法
CommandLine::call 和 CommandLine::run 便利方法现在支持子命令,并将执行用户指定的最后一个子命令。以前,子命令通常被忽略,只执行顶层命令。
改进异常
最后,从此版本开始,所有picocli异常都提供了一个 getCommandLine 方法,
该方法返回解析或执行失败处的命令或子命令。
以前,如果用户对带有子命令的应用提供了无效的输入,那么很难准确地指出哪个子命令未能解析输入。